Alas, for the changes of time! The Fleet, that little, quick-flowing stream, once so bright and clear, is now a sewer! but its name remains immortalised by the street called after it.
Although, according to a modern antiquary, a Roman amphitheatre once stood on the site of the Fleet Prison, and Roman citizens were certainly interred outside Ludgate, we know but little whether Roman buildings ever stood on the west side of the City gates. Stow, however, describes a stone payement supported on piles being found, in 1595, near the Fleet Street end of Chancery Lane; so that we may presume the soil of the neighbourhood was originally marshy. The first British settlers there must probably have been restless spirits, impatient of the high rents and insufficient room inside the City walls and willing, for economy, to risk the forays of any Saxon pirates who chose to steal up the river on a dusky night and sack the outlying cabins of London.
There were certainly rough doings in Fleet Street in the Middle Ages, for the City chronicles tell us of much blood spilt there and of many deeds of violence. In 1228 (Henry III.) we find, for instance, one Henry de Buke slaying a man named Le Ireis, le Tylor, of Fleet Bridge, then fleeing to the church of St. Mary, Southwark, and there claiming sanctuary. In 1311 (Edward II.) five of the king’s not very respectable or law-fearing household were arrested in Fleet Street for a burglary; and though the weak king demanded them (they were perhaps servants of his Gascon favourite, Piers Gaveston, whom the barons afterwards killed), the City refused to give them up, and they probably had short shrive. In the same reign, when the Strand was full of bushes and thickets, Fleet Street could hardly have been much better. Still, the shops in Fleet Street were, no doubt, even in Edward II.’s reign, of importance, for we find, in 1321, a Fleet Street bootmaker supplying the luxurious king with “six pairs of boots, with tassels of silk and drops of silver-gilt, the price of each pair being 5s.” In Richard II.’s reign it is especially mentioned that Wat Tyler’s fierce Kentish men sacked the Savoy church, part of the Temple, and destroyed two forges which had been originally erected on each side of St. Dunstan’s church by the Knight Templars. The Priory of St. John of Jerusalem had paid a rent of 15s. for these forges, which same rent was given for more than a century after their destruction.
The poet Chaucer is said to have beaten a saucy Franciscan friar in Fleet Street, and to have been fined 2s. for the offence by the Honourable Society of the Inner Temple; so Speight had heard from one who had seen the entry in the records of the Inner Temple.
In King Henry IV.’s reign another crime disturbed Fleet Street. A Fleet Street goldsmith was murdered by ruffians in the Strand, and his body thrown under the Temple Stairs.
In 1440 (Henry VI.) a strange procession startled London citizen’s. Eleanor Cobham, Duchess of Gloucester, did penance through Fleet Street for witchcraft practised against the king. She and certain priests and necromancers had, it was said, melted a wax figure of young King Henry before a slow fire, praying that as that figure melted his life might melt also. Of the duchess’s confederates, the Witch of Ely, was burned at Smithfield, a canon of Westminster died in the Tower, and a third culprit was hung, drawn, and quartered at Tyburn. The duchess was brought from Westminster, and landed at the Temple Stairs, from whence, with a tall wax taper in her hand, she walked bareheaded to St. Paul’s, where she offered at the high altar. Another day she did penance at Christ Church, Aldgate; a third day at St. Michael’s, Cornhill, the Lord Mayor, sheriffs, and most of the Corporation following: She was then banished to the Isle of Man, and her ghost they say still haunts Peel Castle.
And now, in the long panorama of years, there rises in Fleet Street a clash of swords and a clatter of bucklers.’ In 1441 (Henry VI.) the general effervescence of the times spread beyond Ludgate, and there was a great affray in Fleet Street between the hot-blooded youths of the Inns of Court and the citizens, which lasted two days; the chief man in the riot was one of Clifford’s Inn, named Harbottle; and this irrepressible Harbottle and his fellows only the appearance of the mayor and sheriffs could quiet. In 1458 (in the same reign) there was a more serious riot of the same kind; the students were then driven back by archers from the Conduit near Shoe Lane to their several inns, and some slain, including “the Queen’s attornie,” who certainly ought to have known better and kept closer to his parchments. Even the king’s meek nature was roused at this, he committed the principal governors of Furnival’s, Clifford’s, and Barnard’s inns, to the castle of Hertford, and sent for several aldermen to Windsor Castle, where he either rated or imprisoned them, or both.
Fleet Street often figures in the chronicles of Elizabeth’s reign. On one visit it is particularly said that she often graciously stopped her coach to speak to the poor; and a green branch of rosemary given to her by a poor woman near Fleet Bridge was seen, not without marvellous wonder of such as knew the presenter, when her Majesty reached Westminster. In the same reign we are told that the young Earl of Oxford, after attending his father’s funeral in Essex, rode through Fleet Street to Westminster, attended by seven score horsemen, all in black. Such was the splendid and proud profusion of Elizabeth’s nobles.
James’s reign was a stormy one for Fleet Street. Many a time the ready ‘prentices snatched their clubs (as we read in “The Fortunes of Nigel”), and, vaulting over their counters, joined in the fray that surged past their shops. In 1621 particularly, three ‘prentices having abused Gondomar, the Spanish ambassador, as he passed their master’s door in Fenchurch Street, the king ordered the riotous youths to be whipped from Aldgate to Temple Bar. In Fleet Street, however, the apprentices rose in force, and shouting “Rescue!” quickly released the lads and beat the marshalmen. If there had been any resistance, another thousand sturdy ‘prentices would soon have carried on the war.
Nor did Charles’s reign bring any quiet to Fleet Street, for then the Templars began to lug out their swords. On the 12th of January, 1627, the Templars, having chosen a Mr. Palmer as their Lord of Misrule, went out late at night into Fleet Street to collect his rents. At every door the jovial collectors winded the Temple horn, and if at the second blast the door was not courteously opened, my lord cried majestically, “Give fire, gunner,” and a sturdy smith burst the pannels open with a huge sledge-hammer. The horrified Lord Mayor being appealed to soon arrived, attended by the watch of the ward and men armed with halberts. At eleven o’clock on the Sunday night the two monarchs came into collision in Hare Alley (now Hare Court). The Lord of Misrule bade my Lord Mayor come to him, but Palmer, omitting to take off his hat, the halberts flew sharply round him, his subjects were soundly beaten, and he was dragged off to the Compter. There, with soiled finery, the new year’s king was kept two days in durance, the attorney-general at last fetching the fallen monarch away in his own coach. At a court masque soon afterwards the king made the two rival potentates join hands; but the King of Misrule had, nevertheless, to refund all the five shillings’ he had exacted, and repair all the Fleet Street doors his too handy gunner had destroyed. The very next year the quarrelsome street broke again into a rage, and four persons lost their lives. Of the rioters, two were executed within the week. One of these was John Stanford, of the duke’s chamber, and the other Captain Nicholas Ashurst. The quarrel was about politics, and the courtiers seem to have been the offenders.
In Charles II.’s time the pillory was sometimes set up at the Temple gate; and here the wretch Titus Oates stood, amidst showers of unsavoury eggs and the curses of those who had learnt to see the horror of his crimes. Well said Judge Withers to this man, “I never pronounce criminal sentence but with some compassion; but you are such a villain and hardened sinner, that I can find no sentiment of compassion for you.” The pillory had no fixed place, for in 1670 we find a Scotchman suffering at the Chancery Lane end for telling a victualler that his house would be fired by the Papists; and the next year a man stood upon the pillory at the end of Shoe Lane for insulting Lord Ambassador Coventry as he was starting for Sweden.
In the reign of Queen Anne those pests of the London streets, the “Mohocks,” seem to have infested Fleet Street. These drunken desperadoes— the predecessors of the roysterers who, in the times of the Regency, “boxed the Charlies,” broke windows, and stole knockers—used to find a cruel pleasure in surrounding a quiet homeward-bound citizen and pricking him with their swords. Addison makes worthy Sir Roger de Coverley as much afraid of these night-birds as Swift himself; and the old baronet congratulates himself on escaping from the clutches of “the emperor and his black men,” who had followed him half-way down Fleet Street. He, however, boasts that he threw them out at the end of Norfolk Street, where he doubled the corner, and scuttled safely into his quiet lodgings.
From Elizabethan times downwards, Fleet Street was a favourite haunt of showmen. Concerning these popular exhibitions Mr. Noble has, with great industry, collected the following curious enumeration:—
“Ben Jonson,” says our trusty authority, “in Every Man in his Humour, speaks of ‘a new motion of the city of Nineveh, with Jonas and the whale, at Fleet Bridge.’ In 1611 ‘the Fleet Street mandrakes’ were to be seen for a penny; and years later the giants of St. Dunstan’s clock caused the street to be blocked up, and people to lose their time, their temper, and their money. During Queen Anne’s reign, however, the wonders of Fleet Street were at their height. In 1702 a model of Amsterdam, thirty feet long by twenty feet wide, which had taken twelve years in making, was exhibited in Bell Yard; a child, fourteen years old, without thighs or legs, and eighteen inches high, was to be seen ‘at the “Eagle and Child,” a grocer’s shop, near Shoe Lane;’ a great Lincolnshire ox, nineteen hands high, four yards long, as lately shown at Cambridge, was on view ‘at the “White Horse,” where the great elephant was seen;’ and ‘between the “Queen’s Head” and “Crooked Billet,” near Fleet Bridge,’ were exhibited daily ‘two strange, wonderful, and remarkable monstrous creatures—an old she-dromedary, seven feet high and ten feet long, lately arrived from Tartary, and her young one; being the greatest rarity and novelty that ever was seen in the three kingdomes before.’ In 1710, at the ‘Duke of Marlborough’s Head,’ in Fleet Street (by Shoe Lane), was exhibited the ‘moving picture’ mentioned in the Tatler; and here, in 1711, ‘the great posture-master of Europe,’ eclipsing the deceased Clarke and Higgins, greatly startled sight-seeing London. ‘He extends his body into all deformed shapes; makes his hip and shoulder-bones meet together; lays his head upon the ground, and turns his body round twice or thrice, without stirring his face from the spot; stands upon one leg, and extends the other in a perpendicular line half a yard above his head; and extends his body from a table with his head a foot below his heels, having nothing to balance his body but his feet; with several other postures too tedious to mention.’
“And here, in 1718, De Hightrehight, the fireeater, ate burning coals, swallowed flaming brimstone, and sucked a red-hot poker, five times a day!
“What will my billiard-loving friends say to the St. Dunstan’s Inquest of the year 1720? ‘Item, we present Thomas Bruce, for suffering a gamingtable (called a billiard-table, where people commonly frequent and game) to be kept in his house.’ A score of years later, at the end of Wine Office Court, was exhibited an automaton clock, with three figures or statues, which at the word of command poured out red or white wine, represented a grocer shutting up his shop and a blackamoor who struck upon a bell the number of times asked. Giants and dwarfs were special features in Fleet Street. At the ‘Rummer,’ in Three Kings’ Court, was to be seen an Essex woman. named Gordon, not nineteen years old, though seven feet high, who died in 1737. At the ‘Blew Boar and Green Tree’ was on view an Italian giantess, above seven feet, weighing 425 lbs., who had been seen by ten reigning sovereigns. In 1768 died, in Shire Lane, Edward Bamford, another giant, seven feet four inches in height, who was buried in St. Dunstan’s, though £200 was offered for his body for dissection. At the ‘Globe,’ in 1717, was shown Matthew Buckinger, a German dwarf, born in 1674, without hands, legs, feet, or thighs, twenty-nine inches high; yet can write, thread a needle, shuffle a pack of cards, play skittles, &c. A facsimile of his writing is among the Harleian MSS. And in 1712 appeared the Black Prince and his wife, each three feet high; and a Turkey horse, two feet odd high and twelve years old, in a box. Modern times have seen giants and dwarfs, but have they really equalled these? In 1822 the exhibition of a mermaid here was put a stop to by the Lord Chamberlain.”
In old times Fleet Street was rendered picturesque, not only by its many gable-ended houses adorned with quaint carvings and plaster stamped in patterns, but also by the countless signs, gay with gilding and painted with strange devices, which hung above the shop-fronts. Heraldry exhausted all its stores to furnish emblems for different trades. Lions blue and red, falcons, and dragons of all colours, alternated with heads of John the Baptist, flying pigs, and hogs in armour. On a windy day these huge masses of painted timber creaked and waved overhead, to the terror of nervous pedestrians, nor were accidents by any means rare. On the 2nd of December, 1718 (Queen Anne), a signboard opposite Bride Lane, Fleet Street, having loosened the brickwork by its weight and movement, suddenly gave way, fell, and brought the house down with it, killing four persons, one of whom was the queen’s jeweller. It was not, however, till 1761 (George II.) that these dangerous signboards were ordered to be placed flat against the walls of the houses.
When Dr. Johnson said, “Come and let us take a walk down Fleet Street,” he proposed a no very easy task. The streets in his early days, in London, had no side-pavements, and were roughly paved, with detestable gutters running down the centre. From these gutters the jumbling coaches of those days liberally scattered the mud on the unoffending pedestrians who happened to be crossing at the time. The sedan-chairs, too, were awkward impediments, and choleric people were disposed to fight for the wall. In 1766, when Lord Eldon came to London as a schoolboy, and put up at that humble hostelry the “White Horse,” in Fetter Lane, he describes coming home from Drury Lane with his brother in a sedan. Turning out of Fleet Street into Fetter Lane, some rough fellows pushed against the chair at the corner and upset it, in their eagerness to pass first. Dr. Johnson’s curious nervous habit of touching every street-post he passed was cured in 1766, by the laying down of side-pavements. On that occasion it is said two English paviours in Fleet Street bet that they would pave more in a day than four Scotchmen could. By three o’clock the Englishmen had got so much ahead that they went into a public-house for refreshment, and, afterwards returning to their work, won the wager.
In the Wilkes’ riot of 1763, the mob burnt a large jack-boot in the centre of Fleet Street, in ridicule of Lord Bute; but a more serious affray took place in this street in 1769, when the noisy Wilkites closed the Bar, to stop a procession of 600 loyal citizens en route to St. James’s to present an address denouncing all attempts to spread sedition and uproot the constitution. The carriages were pelted with stones, and the City marshal, who tried to open the gates, was bedaubed with mud. Mr. Boehm and other loyalists took shelter in “Nando’s Coffee House.” About 150 of the frightened citizens, passing up Chancery Lane, got to the palace by a devious way, a hearse with two white horses and two black following them to St. James’s Palace. Even there the Riot Act had to be read and the Guards sent for. When Mr. Boehm fled into “Nando’s,” in his alarm, he sent home his carriage containing the address. The mob searched the vehicle, but could not find the paper, upon which Mr. Boehm hastened to the Court, and arrived just in time with the important document.
The treason trials of 1794 brought more noise and trouble to Fleet Street. Hardy, the secretary to the London Corresponding Society, was a shoemaker at No. 161; and during the trial of this approver of the French Revolution, Mr. John Scott (afterwards Lord Eldon) was in great danger from a Fleet Street crowd. “The mob,” he says, “kept thickening round me till I came to Fleet Street, one of the worst parts that I had to pass through, and the cries began to be rather threatening. ‘Down with him!’ ‘Now is the time, lads; do for him!’ and various others, horrible enough; but I stood up, and spoke as loud as I could: ‘You may do for me, if you like; but, remember, there will be another Attorney-General before eight o’clock to-morrow morning, and the king will not allow the trials to be stopped.’ Upon this one man shouted out, ‘Say you so? you are right to tell us. Let us give him three cheers, my lads!’ So they actually cheered me, and I got safe to my own door.”
There was great consternation in Fleet Street in November, 1820, when Queen Caroline, attended by 700 persons on horseback, passed publicly through it to return thanks at St. Paul’s. Many alarmed people barricaded their doors and windows. Still greater was the alarm in August, 1821, when the queen’s funeral procession went by, after the deplorable fight with the Horse Guards at Cumberland Gate, when two of the rioters were killed.
With this rapid sketch of a few of the events in the history of Fleet Street, we begin our patient peregrination from house to house.
CHAPTER IV.
FLEET STREET (continued).
Dr. Johnson in Ambuscade at Temple Bar—The First Child—Dryden and Black Will—Rupert’s Jewels—Telson’s Bank—The Apollo Club at the “Devil”—”Old Sir Simon the King”—”Mull Sack”—Dr. Johnson’s Supper to Mrs. Lennox—Will Waterproof at the “Cock”—The Duel at “Dick’s Coffee House”—Lintot’s Shop—Pope and Warburton—Lamb and the Albion—The Palace of Cardinal Wolsey—Mrs. Salmon’s Waxwork—Isaak Walton—Praed’s Bank—Murray and Byron—St.Dunstan’s—Fleet Street Printers—Hoare’s Bank and the “Golden Bottle”—The Real and Spurious “Mitre”—Hone’s Trial—Cobbett’s Shop—”Peele’s Coffee House.”
There is a delightful passage in an almost unknown essay by Dr. Johnson that connects him indissolubly with the neighbourhood of Temple Bar. The essay, written in 1756 for the Universal Visitor, is entitled “A Project for the Employment of Authors,” and is full of humour, which, indeed, those who knew him best considered the chief feature of Johnson’s genius. We rather pride ourselves on the discovery of this pleasant bit of autobiography:—”It is my practice,” says Johnson, “when I am in want of amusement, to place myself for an hour at Temple Bar, or any other narrow pass much frequented, and examine one by one the looks of the passengers, and I have commonly found that between the hours of eleven and four every sixth man is an author. They are seldom to be seen very early in the morning or late in the evening, but about dinner-time they are all in motion, and have one uniform eagerness in their faces, which gives little opportunity of discerning their hopes or fears, their pleasures or their pains. But in the afternoon, when they have all dined, or composed themselves to pass the day without a dinner, their passions have full play, and I can perceive one man wondering at the stupidity of the public, by which his new book has been totally neglected; another cursing the French, who fright away literary curiosity by their threat of an invasion; another swearing at his bookseller, who will advance no money without copy; another perusing as he walks his publisher’s bill; another murmuring at an unanswerable criticism; another determining to write no more to a generation of barbarians; and another wishing to try once again whether he cannot awaken the drowsy world to a sense of his merit.” This extract seems to us to form an admirable companion picture to that in which we have already shown Goldsmith bantering his brother Jacobite, Johnson, as they looked up together at the grim heads on Temple Bar.

DR. TITUS OATES.
That quiet grave house (No. 1), that seems to demurely huddle close to Temple Bar, as if for protection, is the oldest banking-house in London except one. For two centuries gold has been shovelled about in those dark rooms, and reams of bank-notes have been shuffled over by practised thumbs. Private banks originated in the stormy days before the Civil War, when wealthy citizens, afraid of what might happen, entrusted their money to their goldsmiths to take care of till the troubles had blown over. In the reign of Charles I., Francis Child, an industrious apprentice of the old school, married the daughter of his master, William Wheeler, a goldsmith, who lived one door west of Temple Bar, and in due time succeeded to his estate and business. In the first London Directory (1677), among the fifty-eight goldsmiths, thirty-eight of whom lived in Lombard Street, “Blanchard & Child,” at the “Marygold,” Fleet Street, figure conspicuously as “keeping running cashes.” The original Marygold (sometimes mistaken for a rising sun), with the motto, “Ainsi mon ame,” gilt upon a green ground, elegantly designed in the French manner, is still to be seen in the front office, and a marigold in full bloom still blossoms on the bank cheques. In the year 1678 it was at Mr. Blanchard’s, the goldsmith’s, next door to Temple Bar, that Dryden the poet, bruised and angry, deposited £50 as a reward for any one who would discover the bullies of Lord Rochester who had beaten him in Rose Alley for some scurrilous verses really written by the Earl of Dorset. The advertisement promises, if the discoverer be himself one of the actors, he shall still have the £50, without letting his name be known or receiving the least trouble by any prosecution. Black Will’s cudgel was, after all, a clumsy way of making a repartee. Late in Charles II.’s reign Alderman Backwell entered the wealthy firm; but he was ruined by the iniquitous and arbitrary closing of the Exchequer in 1672, when the needy and unprincipled king pocketed at one swoop more than a million and a half of money, which he soon squandered on his shameless mistresses and unworthy favourites. In that quaint room over Temple Bar the firm still preserve the dusty books of the unfortunate alderman, who fled to Holland. There, on the sallow leaves over which the poor alderman once groaned, you can read the items of our sale of Dunkirk to the French, the dishonourable surrender of which drove the nation almost to madness, and hastened the downfall of Lord Clarendon, who was supposed to have built a magnificent house (on the site of Albemarle Street, Piccadilly) with some of the very money. Charles II. himself banked here, and drew his thousands with all the careless nonchalance of his nature. Nell Gwynne, Pepys, of the “Diary,” and Prince Rupert also had accounts at Child’s, and some of these ledgers are still hoarded over Temple Bar in that Venetian-looking room, approached by strange prison-like passages, for which chamber Messrs. Child pay something less than £50 a-year.

TEMPLE BAR AND THE “DEVIL TAVERN” (see page 38).
When Prince Rupert died at his house in the Barbican, the valuable jewels of the old cavalry soldier, valued at £20,000, were disposed of in a lottery, managed by Mr. Francis Child, the goldsmith; the king himself, who took a half-businesslike, half-boyish interest in the matter, counting the tickets among all the lords and ladies at Whitehall.
In North’s “Life of Lord Keeper Guildford,” the courtier and lawyer of the reign of Charles II., there is an anecdote that pleasantly connects Child’s bank with the fees of the great lawyers who in that evil reign ruled in Chancery Lane:—
“The Lord Keeper Guildford’s business increased,” says his biographer, “even while he was solicitor, to be so much as to have overwhelmed one less dexterous; but when he was made AttorneyGeneral, though his gains by his office were great, they were much greater by his practice, for that flowed in upon him like an orage, enough to overset one that had not an extraordinary readiness in business. His skull-caps, which he wore when he had leisure to observe his constitution, as I touched before, were now destined to lie in a drawer, to receive the money that came in by fees. One had the gold, another the crowns and half-crowns, and another the smaller money. When these vessels were full, they were committed to his friend (the Hon. Roger North), who was constantly near him, to tell out the cash and put it into the bags according to the contents; and so they went to his treasurers, Blanchard & Child, goldsmiths, Temple Bar.”
Year by year the second Sir Francis Child grew in honour. He was alderman, sheriff, Lord Mayor, President of Christ’s Hospital, and M.P. for the City, and finally, dying in 1713, full of years, was buried under a grand black marble tomb in Fulham churchyard, and his account closed for ever. The family went on living in the sunshine. Sir Robert, the son of the Sir Francis, was also alderman of his ward; and, on his death, his brother, Sir Francis, succeeded to all his father’s dignities, became an East Indian director, and in 1725 received the special thanks of the citizens for promoting a special act for regulating City elections. Another member of this family (Sir Josiah Child) deserves special mention as one of the earliest writers on political economy and a man much in advance of his time. He saw through the old fallacy about the balance of trade, and explained clearly the true causes of the commercial prosperity of the Dutch. He also condemned the practice of each parish paying for its own poor, an evil which all Poor-law reformers have endeavoured to alter. Sir Josiah was at the head of the East India Company, already feeling its way towards the gold and diamonds of India. His brother was Governor of Bombay, and by the marriage of his numerous daughters the rich merchant became allied to half the peers and peeresses of England. The grandson of Alderman Backwell married a daughter of the second Sir Francis Child, and his daughter married William Praed, the Truro banker, who early in the present century opened a bank at 189, Fleet Street. So, like three strands of a gold chain, the three banking families were welded together. In 1689 Child’s bank seems to have for a moment tottered, but was saved by the timely loan of £1,400 proffered by that overbearing woman the Duchess of Marlborough. Hogarth is said to have made an oil sketch of the scene, which was sold at Hodgson’s sale-room in 1834, and has since disappeared.
In Pennant’s time (1793) the original goldsmith’s shop seems to have still existed in Fleet Street, in connection with this bank. The principal of the firm was the celebrated Countess of Jersey, a former earl having assumed the name of Child on the countess inheriting the estates. of her maternal grandfather, Robert Child, Esq., of Osterly Park, Middlesex. A small full-length portrait of this great beauty of George IV.’s court, painted by Lawrence in his elegant but meretricious manner, hangs in the first-floor room of the old bank. The last Child died early in this century. A descendant of Addison is a member of the present firm. In Chapter 1., Book I., of his “Tale of Two Cities,” Dickens has sketched Child’s bank with quite an Hogarthian force and colour. He has playfully exaggerated the smallness, darkness, and ugliness of the building, of which he describes the partners as so proud; but there is all his usual delightful humour, occasionally passing into caricature:—
“Thus it had come to pass that Telson’s was the triumphant perfection of inconvenience. After bursting open a door of idiotic obstinacy with a weak rattle in its throat, you fell into Telson’s down two steps, and came to your senses in a miserable little shop with two little counters, where the oldest of men made your cheque shake as if the wind rustled it, while they examined the signature by the dingiest of windows, which were always under a showerbath of mud from Fleet Street, and which were made the dingier by their own iron bars and the heavy shadow of Temple Bar. If your business necessitated your seeing ‘the House,’ you were put into a species of Condemned Hold at the back, where you meditated on a mis-spent life, until the House came with its hands in its pockets, and you could hardly blink at it in the dismal twilight.”
In 1788 (George III.) the firm purchased the renowned “Devil Tavern,” next door eastward, and upon the site erected the retiring row of houses up a dim court, now called Child’s Place, finally absorbing the old place of revelry and hushing the unseemly clatter of pewter pots and the clamorous shouts of “Score a pint of sherry in the Apollo” for ever.
The noisy “Devil Tavern” (No. 2, Fleet Street) had stood next the quiet goldsmith’s shop ever since the time of James I. Shakespeare himself must, day after day, have looked up at the old sign of St. Dunstan tweaking the Devil by the nose, that flaunted in the wind near the Bar. Perhaps the sign was originally a compliment to the goldsmith’s men who frequented it, for St. Dunstan was, like St. Eloy, a patron saint of goldsmiths, and himself worked at the forge as an amateur artificer of church plate. It may, however, have only been a mark of respect to the saint, whose church stood hard by, to the east of Chancery Lane. At the “Devil” the Apollo Club, almost the first institution of the kind in London, held its merry meetings, presided over by that grim yet jovial despot, Ben Jonson. The bust of Apollo, skilfully modelled from the head of the Apollo Belvidere, that once kept watch over the door, and heard in its time millions of witty things and scores of fond recollections of Shakespeare by those who personally knew and loved him, is still preserved at Child’s bank. They also show there among their heirlooms “The Welcome,” probably written by immortal Ben himself, which is full of a jovial inspiration that speaks well for the canary at the “Devil.” It used to stand over the chimney-piece, written in gilt letters on a black board, and some of the wittiest and wisest men of the reigns of James and Charles must have read it over their cups. The verses run,—.
“Welcome all who lead or follow
To the oracle of Apollo,” &c.
Beneath these verses some enthusiastic disciple of the author has added the brief epitaph inscribed by an admirer on the crabbed old poet’s tombstone in Westminster Abbey,—
“O, rare Ben Jonson.”
The rules of the club (said to have been originally cut on a slab of black marble) were placed above the fireplace. They were devised by Ben Jonson, in imitation of the rules of the Roman entertainments, collected by the learned Lipsius; and, as Leigh Hunt says, they display the author’s usual style of elaborate and compiled learning, not without a taste of that dictatorial self-sufficiency that made him so many enemies. They were translated by Alexander Brome, a poetical attorney of the day, who was one of Ben Jonson’s twelve adopted poetical sons. We have room only for the first few, to show the poetical character of the club:—
“Let none but guests or clubbers hither come;
Let dunces, fools, and sordid men keep home;
Let learned, civil, merry men b’ invited,
And modest, too; nor be choice liquor slighted.
Let nothing in the treat offend the guest:
More for delight than cost prepare the feast.”
The later rules forbid the discussion of serious and sacred subjects. No itinerant fiddlers (who then, as now, frequented taverns) were to be allowed to obtrude themselves. The feasts were to be celebrated with laughing, leaping, dancing, jests, and songs, and the jests were to be “without reflection.” No man (and this smacks of Ben’s arrogance) was to recite “insipid” poems, and no person was to be pressed to write verse. There were to be in this little Elysium of an evening no vain disputes, and no lovers were to mope about unsocially in corners. No fighting or brawling was to be tolerated, and no glasses or windows broken, or was tapestry to be torn down in wantonness. The rooms were to be kept warm; and, above all, any one who betrayed what the club chose to do or say was to be, nolens volens, banished. Over the clock in the kitchen some wit had inscribed in neat Latin the merry motto, “If the wine of last night hurts you, drink more to-day, and it will cure you”—a happy version of the dangerous axiom of “Take a hair of the dog that bit you.”
At these club feasts the old poet with “the mountain belly and the rocky face,” as he has painted himself, presided, ready to enter the ring against all comers. By degrees the stern man with the worn features, darkened by prison cell and hardened by battle-fields, had mellowed into a Falstaff. Long struggles with poverty had made Ben arrogant, for he had worked as a bricklayer in early life and had served in Flanders as a common soldier; he had killed a rival actor in a duel, and had been in danger of having his nose slit in the pillory for a libel against King James’s Scotch courtiers. Intellectually, too, Ben had reason to claim a sort of sovereignty over the minor poets. His Every Man in his Humour had been a great success; Shakespeare had helped him forward, and been his bosom friend. Parts of his Sejanus, such as the speech of Envy, beginning,—
“Light, I salute thee, but with wounded nerves,
Wishing thy golden splendour pitchy darkness,”
are as sublime as his songs, such as
“Drink to me only with thine eyes,”
are graceful, serious, and lyrical. The great compass of his power and the command he had of the lyre no one could deny; his learning Donne and Camden could vouch for. He had written the most beautiful of court masques; his Bobadil some men preferred to Falstaff. Alas! no Pepys or Boswell has noted the talk of those evenings.
A few glimpses of the meetings we have, and but a few. One night at the “Devil” a country gentleman was boastful of his property. It was all he had to boast about among the poets; Ben, chafed out of all decency and patience, at last roared, “What signify to us your dirt and your clods? Where you have an acre of land I have ten acres of wit!” “Have you so, good Mr. Wise-acre,” retorted Master Shallow. “Why, now, Ben,” cried out a laughing friend, “you seem to be quite stung.” “I’ faith, I never was so pricked by a hobnail before,” growled Ben, with a surly smile.
Another story records the first visit to the “Devil” of Randolph, a clever poet and dramatist, who became a clergyman, and died young. The young poet, who had squandered all his money away in London pleasures, on a certain night, before he returned to Cambridge, resolved to go and see Ben and his associates at the “Devil,” cost what it might. But there were two great obstacles—he was poor, and he was not invited. Nevertheless, drawn magnetically by the voices of the illustrious men in the Apollo, Randolph at last peeped in at the door among the waiters. Ben’s quick eye soon detected the eager, pale face and the scholar’s threadbare habit. “John Bo-peep,” he shouted, “come in!” a summons Randolph gladly obeyed. The club-men instantly began rhyming on the meanness of the intruder’s dress, and told him if he could not at once make a verse he must call for a quart of sack. There being four of his tormentors, Randolph, ready enough at such work, replied as quick as lightning:—
“I, John Bo-peep, and you four sheep,
With each one his good fleece;
If that you are willing to give me your shilling,
‘Tis fifteen pence apiece.”
“By the Lord!” roared the giant president, “I believe this is my son Randolph!” and on his owning himself, the young poet was kindly entertained, spent a glorious evening, was soaked in sack, “sealed of the tribe of Ben,” and became one of the old poet’s twelve adopted sons.
Shakerley Marmion, a contemporary dramatist of the day, has left a glowing Rubenesque picture of the Apollo evenings, evidently coloured from life. Careless, one of his characters, tells his friends he is full of oracles, for he has just come from Apollo. “From Apollo?” says his wondering friend. Then Careless replies, with an inspired fervour worthy of a Cavalier poet who fought bravely for King Charles:—
“From the heaven
Of my delight, where the boon Delphic god
Drinks sack and keep his bacchanalia,
And has his incense and his altars smoking,
And speaks in sparkling prophecies; thence I come,
My brains perfumed with the rich Indian vapour,
And heightened with conceits. . . . .
And from a mighty continent of pleasure
Sails thy brave Careless.”
Simon Wadloe, the host of the “Devil,” who died in 1627, seems to have been a witty butt of a man, much such another as honest Jack Falstaff; a merry boon companion, not only witty himself, but the occasion of wit in others, quick at repartee, fond of proverbial sayings, curious in his wines. A good old song, set to a fine old tune, was written about him, and called “Old Sir Simon the King.” This was the favourite old-fashioned ditty in which Fielding’s rough and jovial Squire Western afterwards delighted.
Old Simon’s successor, John Wadloe (probably his son), made a great figure at the Restoration procession by heading a band of young men all dressed in white. After the Great Fire John rebuilt the “Sun Tavern,” behind the Royal Exchange, and was loyal, wealthy, and foolish enough to lend King Charles certain considerable sums, duly recorded in Exchequer documents, but not so duly paid.
In the troublous times of the Commonwealth the “Devil” was the favourite haunt of John Cottington, generally known as “Mull Sack,” from his favourite beverage of spiced sherry negus. This impudent rascal, a sweep who had turned highwayman, with the most perfect impartiality rifled the pockets alternately of Cavaliers and Roundheads. Gold is of no religion; and your true cut-purse is of the broadest and most sceptical Church. He emptied the pockets of Lord Protector Cromwell one day, and another he stripped Charles II., then a Bohemian exile at Cologne, of plate valued at £1,500. One of his most impudent exploits was stealing a watch from Lady Fairfax, that brave woman who had the courage to denounce, from the gallery at Westminster Hall, the persons whom she considered were about to become the murderers of Charles I. “This lady” (and a portly handsome woman she was, to judge by the old portraits), says a pamphlet-writer of the day, “used to go to a lecture on a week-day to Ludgate Church, where one Mr. Jacomb preached, being much followed by the Puritans. Mull Sack, observing this, and that she constantly wore her watch hanging by a chain from her waist, against the next time she came there dressed himself like an officer in the army; and having his comrades attending him like troopers, one of them takes off the pin of a coach-wheel that was going upwards through the gate, by which means it falling off, the passage was obstructed, so that the lady could not alight at the church door, but was forced to leave her coach without. Mull Sack, taking advantage of this, readily presented himself to her ladyship, and having the impudence to take her from her gentleman usher who attended her alighting, led her by the arm into the church; and by the way, with a pair of keen sharp scissors for the purpose, cut the chain in two, and got the watch clear away, she not missing it till the sermon was done, when she was going to see the time of the day.”
The portrait of Mull Sack has the following verses beneath:—
“I walk the Strand and Westminster, and scorn
To march i’ the City, though I bear the horn.
My feather and my yellow band accord,
To prove me courtier; my boot, spur, and sword,
My smoking-pipe, scarf, garter, rose on shoe,
Show my brave mind t’ affect what gallants do.
I sing, dance, drink, and merrily pass the day,
And, like a chimney, sweep all care away.”
In Charles II.’s time the “Devil” became frequented by lawyers and physicians. The talk now was about drugs and latitats, jalap and the law of escheats. Yet, still good company frequented it, for Steele describes Bickerstaff’s sister Jenny’s wedding entertainment there in October, 1709; and in 1710 (Queen Anne) Swift writes one of those charming letters to Stella to tell her that he had dined on October 12th at the “Devil,” with Addison and Dr. Garth, when the good-natured doctor, whom every one loved, stood treat, and there must have been talk worth hearing. In the Apollo chamber the intolerable court odes of Colley Cibber, the poet laureate, used to be solemnly rehearsed with fitting music; and Pope, in “The Dunciad,” says, scornfully:—
“Back to the ‘Devil’ the loud echoes roll,
And ‘Coll’ each butcher roars in Hockly Hole.”
But Colley had talent and he had brass, and it took many such lines to put him down. A good epigram on these public recitations runs thus:—
“When laureates make odes, do you ask of what sort?
Do you ask if they’re good or are evil?
You may judge: from the ‘Devil’ they come to the Court,
And go from the Court to the ‘Devil.'”
Dr. Kenrick afterwards gave lectures on Shakespeare at the Apollo. This Kenrick, originally a rulemaker, and the malicious assailant of Johnson and Garrick, was the Croker of his day. He originated the London Review, and when he assailed Johnson’s “Shakespeare,” Johnson laughingly replied, “That he was not going to be bound by Kenrick’s rules.”
In 1746 the Royal Society held its annual dinner in the old consecrated room, and in the year 1752 concerts of vocal and instrumental music were given in the same place. It was an upstairs chamber, probably detached from the tavern, and lay up a “close,” or court, like some of the old Edinburgh taverns.
The last ray of light that fell on the “Devil” was on a memorable spring evening in 1751. Dr. Johnson (aged forty-two), then busy all day with his six amanuenses in a garret in Gough Square compiling his Dictionary, at night enjoyed his elephantine mirth at a club in Ivy Lane, Paternoster Row. One night at the club, Johnson proposed to celebrate the appearance of Mrs. Lennox’s first novel, “The Life of Harriet Stuart,” by a supper at the “Devil Tavern.” Mrs. Lennox was a lady for whom Johnson—ranking her afterwards above Mrs. Carter, Mrs. Hannah More, or even his favourite, Miss Burney—had the greatest esteem. Sir John Hawkins, that somewhat malign rival of Boswell, describes the night in a manner, for him, unusually genial. “Johnson,” says Hawkins (and his words are too pleasant to condense), “proposed to us the celebrating the birth of Mrs. Lennox’s first literary child, as he called her book, by a whole night spent in festivity. Upon his mentioning it to me, I told him I had never sat up a night in my life; but he continuing to press me, and sayingthat I should find great delight in it, I, as did all the rest of the company, consented.” (The club consisted of Hawkins, an attorney; Dr. Salter, father of a master of the Charter House; Dr. Hawkesworth, a popular author of the day; Mr. Ryland, a merchant; Mr. John Payne, a bookseller; Mr. Samuel Dyer, a young man training for a Dissenting minister; Dr. William M’Ghie, a Scotch physician; Dr. Barker and Dr. Bathurst, youngphysicians.) “The place appointed was the ‘Devil Tavern;’ and there, about the hour of eight, Mrs. Lennox and her husband (a tide-waiter in the Customs), a lady of her acquaintance, with the club. and friends, to the number of twenty, assembled. The supper was elegant; Johnson had directed that a magnificent hot apple-pie should make a part of it, and this he would have stuck with bay leaves, because, forsooth, Mrs. Lennox was an authoress and had written verses; and, further, he had prepared for her a crown of laurel, with which, but not till he had invoked the Muses by some ceremonies of his own invention, he encircled her brows. The night passed, as must be imagined, in pleasant conversation and harmless mirth, intermingled at different periods with the refreshment of coffee and tea. About five a.m., Johnson’s face shone with meridian splendour, though his drink had been only lemonade; but the far greater part of the company had deserted the colours of Bacchus, and were with difficulty rallied to partake of a second refreshment of coffee, which was scarcely ended when the day began to dawn. This phenomenon began to put us in mind of our reckoning; but the waiters were all so overcome with sleep that it was two hours before a bill could be had, and it was not till near eight that the creaking of the street-door gave the signal of our departure.” How one longs to dredge up some notes of such a night’s conversation from the cruel river of oblivion! The Apollo Court, on the opposite side of Fleet Street, still preserves the memory of the great club-room at the “Devil.”

TEMPLE BAR IN DR.JOHNSON’S TIME (see page 29).
In 1764, on an Act passing for the removal of the dangerous projecting signs, the weather-beaten picture of the saint, with the Devil gibbering over his shoulder, was nailed up flat to the front of the old gable-ended house. In 1775, Collins, a public lecturer and mimic, gave a satirical lecture at the “Devil” on modern oratory. In 1776 some young lawyers founded there a Pandemonium Club; and after that there is no further record of the “Devil” till it was pulled down and annexed by the neighbouring bankers. In Steele’s time there was a “Devil Tavern” at Charing Cross, and a rival “Devil Tavern” near St. Dunstan’s; but these competitors made no mark.

MULL SACK AND LADY FAIRFAX. (see page 40).
The “Cock Tavern” (201), opposite the Temple, has been immortalised by Tennyson as thoroughly as the “Devil” was by Ben Jonson. The playful verses inspired by a pint of generous port have made
“The violet of a legend blow
Among the chops and steaks”
for ever, though old Will Waterproof has long since descended for the last time the well-known cellarstairs. The poem which has embalmed his name was, we believe, written when Mr. Tennyson had chambers in Lincoln’s Inn Fields. At that time the room was lined with wainscoting, and the silver tankards of special customers hung in glittering rows in the bar. This tavern was shut up at the time of the Plague, and the advertisement announcing such closing is still extant. Pepys, in his “Diary,” mentions bringing pretty Mrs. Knipp, an actress, of whom his wife was very jealous, here; and the gay couple “drank, eat a lobster, and sang, and mighty merry till almost midnight.” On his way home to Seething Lane, the amorous Navy Office clerk with difficulty avoided two thieves with clubs, who met him at the entrance into the ruins of the Great Fire near St. Dunstan’s. These dangerous meetings with Mrs. Knipp went on till one night Mrs. Pepys came to his bedside and threatened to pinch him with the red-hot tongs. The waiters at the “Cock” are fond of showing visitors one of the old tokens of the house in the time of Charles II. The old carved chimneypiece is of the age of James I.; and there is a doubtful tradition that the gilt bird that struts with such self-serene importance over the portal was the work of that great carver, Grinling Gibbons.
“Dick’s Coffee House” (No. 8, south) was kept in George II.’s time by a Mrs. Yarrow and her daughter, who were much admired by the young Templars who patronised the place. The Rev. James Miller, reviving an old French comedietta by Rousseau, called “The Coffee House,” and introducing malicious allusions to the landlady and her fair daughter, so exasperated the young barristers that frequented “Dick’s,” that they went in a body and hissed the piece from the boards. The author then wrote an apology, and published the play; but unluckily the artist who illustrated it took the bar at “Dick’s” as the background of his sketch. The Templars went madder than ever at this, and the Rev. Miller, who translated Voltaire’s “Mahomet” for Garrick, never came up to the surface again. It was at “Dick’s” that Cowper the poet showed the first symptoms of derangement. When his mind was off its balance he read a letter in a newspaper at “Dick’s,” which he believed had been written to drive him to suicide. He went away and tried to hang himself; the garter breaking, he then resolved to drown himself; but, being hindered by some occurrence, repented for the moment. He was soon after sent to a madhouse in Huntingdon.
In 1681 a quarrel arose between two hot-headed gallants in “Dick’s” about the size of two dishes they had both seen at the “St. John’s Head” in Chancery Lane. The matter eventually was roughly ended at the “Three Cranes” in the Vintry—a tavern mentioned by Ben Jonson—by one of them, Rowland St. John, running his companion, John Stiles, of Lincoln’s Inn, through the body. The St. Dunstan’s Club, founded in 1796, holds its dinner at “Dick’s.”
The “Rainbow Tavern” (No. 15, south) was the second coffee-house started in London. Four years before the Restoration, Mr. Farr, a barber, began the trade here, trusting probably to the young Temple barristers for support. The vintners grew jealous, and the neighbours, disliking the smell of the roasting coffee, indicted Farr as a nuisance. But he persevered, and the Arabian drink became popular. A satirist had soon to write regretfully,—
“And now, alas! the drink has credit got,
And he’s no gentleman that drinks it not.”
About 1780, according to Mr. Timbs, the “Rainbow” was kept by Alexander Moncrieff, grandfather of the dramatist who wrote Tom and Jerry.
Bernard Lintot, the bookseller, who published Pope’s “Homer,” lived in a shop between the two Temple gates (No. 16). In an inimitable letter to the Earl of Burlington, Pope has described how Lintot (Tonson’s rival) overtook him once in Windsor Forest, as he was riding down to Oxford. When they were resting under a tree in the forest, Lintot, with a keen eye to business, pulled out “a mighty pretty ‘Horace,'” and said to Pope, “What if you amused yourself in turning an ode till we mount again?” The poet smiled, but said nothing. Presently they remounted, and as they rode on Lintot stopped short, and broke out, after a long silence: “Well, sir, how far have we got?” “Seven miles,” replied Pope, naively. He told Pope that by giving the hungry critics a dinner of a piece of beef and a pudding, he could make them see beauties in any author he chose. After all, Pope did well with Lintot, for he gained £5,320 by his “Homer.” Dr. Young, the poet, once unfortunately sent to Lintot a letter meant for Tonson, and the first words that Lintot read were: “That Bernard Lintot is so great a scoundrel.” In the same shop, which was then occupied by Jacob Robinson, the publisher, Pope first met Warburton. An interesting account of this meeting is given by Sir John Hawkins, which it may not be out of place to quote here. “The friendship of Pope and Warburton,” he says, “had its commencement in that bookseller’s shop which is situate on the west side of the gateway leading down the Inner Temple Lane. Warburton had some dealings with Jacob Robinson, the publisher, to whom the shop belonged, and may be supposed to have been drawn there on business; Pope might have made a call of the like kind. However that may be, there they met, and entering into conversation, which was not soon ended, conceived a mutual liking, and, as we may suppose, plighted their faith to each other. The fruit of this interview, and the subsequent communications of the parties, was the publication, in November, 1739, of a pamphlet with this title, ‘A Vindication of Mr. Pope’s “Essay on Man,” by the Author of “The Divine Legation of Moses.” Printed for J. Robinson.'” At the Middle Temple Gate, Benjamin Motte, successor to Ben Tooke, published Swift’s “Gulliver’s Travels,” for which he had grudgingly given only £200.
The third doorfrom Chancery Lane (No. 197, north side), Mr. Timbs points out, was in Charles II.’s time a tombstone-cutter’s; and here, in 1684, Howel, whose “Letters” give us many curious pictures of his time, saw a huge monument to four of the Oxenham family, at the death of each of whom a white bird appeared fluttering about their bed. These miraculous occurrences had taken place at a town near Exeter, and the witnesses names duly appeared below the epitaph. No. 197 was afterwards Rackstrow’s museum of natural curiosities and anatomical figures; and the proprietor put Sir Isaac Newton’s head over the door for a sign. Among other prodigies was the skeleton of a whale more than seventy feet long. Donovan, a naturalist, succeeded Rackstrow (who died in 1772) with his London museum. Then, by a harlequin change, No. 197 became the office of the Albion newspaper. Charles Lamb was turned over to this journal from the Morning Post. The editor, John Fenwick, the “Bigot” of Lamb’s “Essay,” was a needy, sanguine man, who had purchased the paper of a person named Lovell, who had stood in the pillory for a libel against the Prince of Wales. For a long time Fenwick contrived to pay the Stamp Office dues by money borrowed from compliant friends. “We,” says Lamb, in his delightful way, “attached our small talents to the forlorn fortunes of our friend. Our occupation was now to write treason.” Lamb hinted at possible abdications. Blocks, axes, and Whitehall tribunals were covered with flowers of so cunning a periphrasis—as, Mr. Bayes says, never naming the thing directly—that the keen eye of an Attorney-General was insufficient to detect the lurking snake among them.
At the south-west corner of Chancery Lane (No. 193) once stood an old house said to have been the residence of that unfortunate reformer, Sir John Oldcastle, Baron Cobham, who was burnt in St. Giles’s Fields in 1417 (Henry V.) In Charles II.’s reign the celebrated Whig Green Ribbon Club used to meet here, and from the balcony flourish their periwigs, discharge squibs, and wave torches, when a great Protestant procession passed by, to burn the effigy of the Pope at the Temple Gate. The house, five stories high and covered with carvings, was pulled down for City improvements in 1799.
Upon the site of No. 192 (east corner of Chancery Lane) the father of Cowley, that fantastic poet of Charles II.’s time, it is said carried on the trade of a grocer. In 1740 a later grocer there sold the finest caper tea for 24s. per lb., his fine green for 18s. per lb., hyson at 16s. per lb., and bohea at 7s. per lb.
No house in Fleet Street has a more curious pedigree than that gilt and painted, shop opposite Chancery Lane (No. 17, south side), falsely called “the palace of Henry VIII. and Cardinal Wolsey.” It was originally the office of the Duchy of Cornwall, in the reign of James I. It is just possible that it was the house originally built by Sir Amyas Paulet, at Wolsey’s command, in resentment for Sir Amyas having set Wolsey, when a mere parish priest, in the stocks for a brawl. Wolsey, at the time of the ignominious punishment, was schoolmaster to the children of the Marquis of Dorset. Paulet was confined to this house for five or six years, to appease the proud cardinal, who lived in Chancery Lane. Sir Amyas rebuilt his prison, covering the front with badges of the cardinal. It was afterwards “Nando’s,” a famous coffee-house, where Thurlow picked up his first great brief. One night Thurlow, arguing here keenly about the celebrated Douglas case, was heard by some lawyers with delight, and the next day, to his astonishment, was appointed junior counsel. This cause won him a silk gown, and so his fortune was made by that one lucky night at “Nando’s.” No. 17 was afterwards the place where Mrs. Salmon (the Madame Tussaud of early times) exhibited her waxwork kings and queens. There was a figure on crutches at the dcor; and Old Mother Shipton, the witch, kicked the astonished visitor as he left. Mrs. Salmon died in 1812. The exhibition was then sold for £500, and removed to Water Lane. When Mrs. Salmon first removed from St. Martin’sle-Grand to near St. Dunstan’s Church, she announced, with true professional dignity, that the new locality “was more convenient for the quality’s coaches to stand unmolested.” Her “Royal Court of England” included 150 figures. When the exhibition removed to Water Lane, some thieves one night got in, stripped the effigies of their finery, and broke half of them, throwing them into a heap that almost touched the ceiling.
Tonson, Dryden’s publisher, commenced business at the “Judge’s Head,” near the Inner Temple gate, so that when at the Kit-Kat Club he was not far from his own shop. One day Dryden, in a rage, drew the greedy bookseller with terrible force:—
“With leering looks, bull-faced, and speckled fair,
With two left legs and Judas-coloured hair,
And frowzy pores that taint the ambient air.”
The poet promised a fuller portrait if the “dog” tormented him further.
Opposite Mrs. Salmon’s, two doors west of old Chancery Lane, till 1799, when the lawyer’s lane was widened, stood an old, picturesque, gabled house, which was once the milliner’s shop kept, in 1624, by that good old soul, Isaak Walton. He was on the Vestry Board of St. Dunstan’s, and was constable and overseer for the precinct next Temple Bar; and on pleasant summer evenings he used to stroll out to the Tottenham fields, rod in hand, to enjoy the gentle sport which he so much loved. He afterwards (1632) lived seven doors up Chancery Lane, west side, and there married the sister of that good Christian, Bishop Ken, who wrote the “Evening Hymn,” one of the most simply beautiful religious poems ever written. It is pleasant in busy Fleet Street to think of the good old citizen on his guileless way to the river Lea, conning his verses on the delights of angling.
Praed’s Bank (No. 189, north side) was founded early in the century by Mr. William Praed, a banker of Truro. The house had been originally the shop of Mrs. Salmon, till she moved to opposite Chancery Lane, and her wax kings and frail queens were replaced by piles of strong boxes and chests of gold. The house was rebuilt in 1802, from the designs of Sir John Soane, whose curious museum still exists in Lincoln’s Inn Fields. Praed, that delightful poet of society, was of the banker’s family, and in him the poetry of refined wealth found a fitting exponent. Fleet Street, indeed, is rich in associations connected with bankers and booksellers; for at No. 19 (south side) we come to Messrs. Gosling’s. This bank was founded in 1650 by Henry Pinckney, a goldsmith, at the sign of the “Three Squirrels”—a sign still to be seen in the ironwork over the centre window. The original sign of solid silver, about two feet in height, made to lock and unlock, was discovered in the house in 1858. It had probably been taken down on the general removal of out-door signs and forgotten. In a secret service-money account of the time of Charles II., there is an entry of a sum of £646 8s. 6d. for several parcels of gold and silver lace bought of William Gosling and partners by the fair Duchess of Cleveland, for the wedding clothes of the Lady Sussex and Lichfield.
No. 32 (south side), still a bookseller’s, was originally kept for forty years by William Sandby, one of the partners of Snow’s bank in the Strand. He sold the business and goodwill in 1762 for £400, to a lieutenant of the Royal Navy, named John M’Murray, who, dropping the Mac, became the well-known Tory publisher. Murray tried in vain to induce Falconer, the author of “The Shipweck,” to join him as a partner. The first Murray died in 1793. In 1812 John Murray, the son of the founder, removed to 50, Albemarle Street. In the Athenæum of 1843 a writer describes how Byron used to stroll in here fresh from his fencing-lessons at Angelo’s or his sparringbouts with Jackson. He was wont to make cruel lunges with his stick at what he called “the spruce books” on Murray’s shelves, generally striking the doomed volume, and by no means improving the bindings. “I was sometimes, as you will guess,” Murray used to say with a laugh, “glad to get rid of him.” Here, in 1807, was published “Mrs. Rundell’s Domestic Cookery;” in 1809, theQuarterly Review; and, in 1811, Byron’s “Childe Harold.”
The original Columbarian Society, long since extinct, was born at offices in Fleet Street, near St. Dunstan’s. This society was replaced by the Pholoperisteron, dear to all pigeon-fanciers, which held its meetings at “Freemasons’ Tavern,” and eventually amalgamated with its rival, the National Columbarian, the fruitful union producing the National Peristeronic Society, now a flourishing institution, meeting periodically at “Evans’s,” and holding a great fluttering and most pleasant annual show at the Crystal Palace. It is on these occasions that clouds of carrier-pigeons are let off, to decide the speed with which the swiftest and besttrained bird can reach a certain spot (a flight, of course, previously known to the bird), generally in Belgium.
The first St. Dunstan’s Church—”in the West,” as it is now called, to distinguish it from one near Tower Street—was built prior to 1237. The present building was erected in 1831. The older church stood thirty feet forward, blocking the carriage-way, and shops with projecting signs were built against the east and west walls. The churchyard was a favourite locality for booksellers. One of the most interesting stories connected with the old building relates to Felton, the fanatical assassin of the Duke of Buckingham, the favourite of Charles I. The murderer’s mother and sisters lodged at a haberdasher’s in Fleet Street, and were attending service in St. Dunstan’s Church when the news arrived from Portsmouth; they swooned away when they heard the name of the assassin. Many of the clergy of St. Dunstan’s have been eminent men. Tyndale, the translator of the New Testament, did duty here. The poet Donne was another of the St. Dunstan’s worthies; and Sherlock and Romaine both lectured at this church. The rectory house, sold in 1693, was No. 183. The clock of old St. Dunstan’s was one of the great London sights in the last century. The giants that struck the hours had been set up in 1671, and were made by Thomas Harrys, of Water Lane, for £35 and the old clock. Lord Hertford purchased them, in 1830, for £210, and set them up at his villa in Regent’s Park. When a child he was often taken to see them; and he then used to say that some day he would buy “those giants.” Hatton, writing in 1708, says that these figures were more admired on Sundays by the populace than the most eloquent preacher in the pulpit within; and Cowper, in his “Table Talk,” cleverly compares dull poets to the St. Dunstan’s giants:—
“When labour and when dulness, club in hand,
Like the two figures at St. Dunstan stand,
Beating alternately, in measured time,
The clock-work tintinnabulum of rhyme.”
The most interesting relic of modern St. Dunstan’s is that unobtrusive figure of Queen Elizabeth at the east end. This figure from the old church came from Ludgate when the City gates were destroyed in 1786. It was bought for £16 10s. when the old church came to the ground, and was re-erected over the vestry entrance. The companion statues of King Lud and his two sons were deposited in the parish bone-house. On one occasion when Baxter was preaching in the old church of St. Dunstan’s, there arose a panic among the audience from two alarms of the building falling. Every face turned pale; but the preacher, full of faith, sat calmly down in the pulpit till the panic subsided, then, resuming his sermon, said reprovingly, “We are in the service of God, to prepare ourselves that we may be fearless at the great noise of the dissolving world when the heavens shall pass away and the elements melt with fervent heat.”
Mr. Noble, in his record of this parish, has remarked on the extraordinary longevity attained by the incumbents of St. Dunstan’s. Dr. White held the living for forty-nine years; Dr. Grant, for fifty-nine; the Rev. Joseph Williamson (Wilkes’s chaplain) for forty-one years; while the Rev. William Romaine continued lecturer for forty-six years. The solution of the problem probably is that a good and secure income is the best promoter of longevity. Several members of the great banking family of Hoare are buried in St. Dunstan’s; but by far the most remarkable monument in the church bears the following inscription:—
“Hobson Judkins, Esq., late of Clifford’s Inn, the Honest Solicitor, who departed this life June 30, 1812. This tablet was erected by his clients, as a token of gratitude and respect for his honest, faithful, and friendly conduct to them throughout life. Go, reader, and imitate Hobson Judkins.”
Among the burials at St. Dunstan’s noted in the registers, the following are the most remarkable:—1559–60, Doctor Oglethorpe, the Bishop of Carlisle, who crowned Queen Elizabeth; 1664, Dame Bridgett Browne, wife of Sir Richard Browne, major-general of the City forces, who offered £1,000 reward for the capture of Oliver Cromwell; 1732, Christopher Pinchbeck, the inventor of the metal named after him and a maker of musical clocks. The Plague seems to have made great havoc in St. Dunstan’s, for in 1665, out of 856 burials, 568 in only three months are marked “P.,” for Plague. The present church, built in 1830–3, was designed by John Shaw, who died on the twelfth day after the completion of the outer shell, leaving his son to finish his work. The church is of a flimsy Gothic, the true revival having hardly then commenced. The eight bells are from the old church. The two heads over the chief entrance are portraits of Tyndale and Dr. Donne; and the painted window is the gift of the Hoare family.
According to Aubrey, Drayton, the great topographical poet, lived at “the bay-window house next the east end of St. Dunstan’s Church.” Now it is a clearly proved fact that the Great Fire stopped just three doors east of St. Dunstan’s, as did also, Mr. Timbs says, another remarkable fire in 1730; so it is not impossible that the author of “The Polyolbion,” that good epic poem, once lived at the present No. 180, though the next house eastward is certainly older than its neighbour. We have given a drawing of the house.
That shameless rogue, Edmund Curll, lived at the “Dial and Bible,” against St. Dunstan’s Church. When this clever rascal was put in the pillory at Charing Cross, he persuaded the mob he was in for a political offence, and so secured the pity of the crowd. The author of “John Buncle” describes Curll as a tall, thin, awkward man, with goggle eyes, splay feet, and knock-knees. His translators lay three in a bed at the “Pewter Platter Inn” at Holborn. He published the most disgraceful books and forged letters. Curll, in his revengeful spite, accused Pope of pouring an emetic into his half-pint of canary when he and Curll and Lintot met by appointment at the “Swan Tavern,” Fleet Street. By St. Dunstan’s, at the “Homer’s Head,” also lived the publisher of the first correct edition of “The Dunciad.”

MRS. SALMON’S WAXWORK, FLEET STREET;”PLACE OF HENRY VIII. AND CARDINAL WOLSEY” (see page 45).
Among the booksellers who crowded round old St. Dunstan’s were Thomas Marsh, of the “Prince’s Arms,” who printed Stow’s “Chronicles;” and William Griffith, of the “Falcon,” in St. Dunstan’s Churchyard, who, in the year 1565, issued, without the authors’ consent, Gorboduc, written by Thomas Norton and Lord Buckhurst, the first real English tragedy and the first play written in English blank verse. John Smethwicke, a still more honoured name, “under the diall” of St. Dunstan’s Church, published “Hamlet” and “Romeo and Juliet.” Richard Marriot, another St. Dunstan’s bookseller, published Quarle’s “Emblems,” Dr. Donne’s “Sermons,” that delightful, simple-hearted book, Isaak Walton’s “Complete Angler,” and Butler’s “Hudibras,” that wonderful mass of puns and quibbles, pressed close as potted meat. Matthias Walker, a St. Dunstan’s bookseller, was one of the three timid publishers who ventured on a certain poem, called “The Paradise Lost,” giving John Milton, the blind poet, the enormous sum of £5 down, £5 on the sale of 1,300 copies of the first, second, and third impressions, in all the munificent recompense of £20; the agreement was given to the British Museum in 1852, by Samuel Rogers, the banker poet.

ST. DUNSTAN’S CLOCK (see page 47).
Nor in this list of Fleet Street printers must we forget to insert Richard Pynson, from Normandy, who had worked at Caxton’s press, and was a contemporary of De Worde. According to Mr. Noble (to whose work we are so deeply indebted), Pynson printed in Fleet Street, at his office, the “George” (first in the Strand, and afterwards beside St. Dunstan’s Church), no less than 215 works The first of these, completed in the year 1483, was probably the first book printed in Fleet Street, afterwards a gathering-place for the ink-stained craft. A copy of this book, “Dives and Pauper,” was sold a few years since for no less than £49. In 1497 the same busy Frenchman published an edition of “Terence,” the first Latin classic printed in England. In 1508 he became printer to King Henry VII., and after this produced editions of Fabyan’s and Froissart’s “Chronicles.” He seems to have had a bitter feud with a rival printer, named Robert Rudman, who pirated his trade-mark. In one of his books he thus quaintly falls foul of the enemy: “But truly Rudeman, because he is the rudest out of a thousand men. . . . . Truly I wonder now at last that he hath confessed it in his own typography, unless it chanced that even as the devil made a cobbler a mariner, he made him a printer. Formerly this scoundrel did prefer himself a bookseller, as well skilled as if he had started forth from Utopia. He knows well that he is free who pretendeth to books, although it be nothing more.”
To this brief chronicle of early Fleet Street printers let us add Richard Bancks, who, in 1600, at his office, “the sign of the White Hart,” printed that exquisite fairy poem, Shakespeare’s “Midsummer Night’s Dream.” How one envies the “reader” of that office, the compositors—nay, even the sable imp who pulled the proof, and snatched a passage or two about Mustard and Pease Blossom in a surreptitious glance! Another great Fleet Street printer was Richard Grafton, the printer, as Mr. Noble says, of the first correct folio English translation of the Bible, by permission of Henry VIII. When in Paris, Grafton had to fly with his books from the Inquisition. After his patron Cromwell’s execution, in 1540, Grafton was sent to the Fleet for printing Bibles, but in the happier times of Edward VI. he became king’s printer at the Grey Friars (now Christ’s Hospital). His former fellowworker in Paris, Edward Whitchurch, set up his press at De Worde’s old house, the “Sun,” near the Fleet Street conduit. He published the “Paraphrase of Erasmus,” a copy of which, Mr. Noble says, existed, with its desk-chains, in the vestry of St. Benet’s, Gracechurch Street. Whitchurch married the widow of Archbishop Cranmer.
The “Hercules Pillars” (now No. 27, Fleet Street, south) was a celebrated tavern as early as the reign of James I., and in the now nameless alley by its side several houses of entertainment nestled themselves. The tavern is interesting to us chiefly because it was a favourite resort of Pepys, who frequently mentions it in his quaint and graphic way.
No. 37 (Hoare’s Bank), south, is well known by the golden bottle that still hangs, exciting curiosity, over the fanlight of the entrance. Popular legend has it that this gilt case contains the original leather bottle carried by the founder when he came up to London, with the usual half-crown in his pocket, to seek his fortune. Sir Richard Colt Hoare, how ever, in his family history, destroys this romance. The bottle is merely a sign adopted by James Hoare, the founder of the bank, from his father having been a citizen and cooper of the city of London. James Hoare was a goldsmith who kept “running cash” at the “Golden Bottle” in Cheapside in 1677. The bank was removed to Fleet Street between 1687 and 1692. The original bank, described by Mr. Timbs as “a low-browed building with a narrow entrance,” was pulled down about forty years since. In the records of the debts of Lord Clarendon is the item, “To Mr. Hoare, for plate, £27 10s. 3d.”; and, by the secret service expenses of James II., “Charles Duncombe and James Hoare, Esqrs.,” appear to have executed for a time the office of master-workers at the Mint. A Sir Richard Hoare was Lord Mayor in 1713; and another of the same family, sheriff in 1740–41 and Lord Mayor in 1745, distinguished himself by his preparations to defend London against the Pretender. In an autobiographical record still extant of the shrievalty of the first of these gentlemen, the writer says:—” After being regaled with sack and walnuts, I returned to my own house in Fleet Street, in my private capacity, to my great consolation and comfort.” This Richard Hoare, with Beau Nash, Lady Hastings, &c., founded, in 1716, the Bath General Hospital, to which charity the firm still continue treasurers; and to this same philanthropic gentleman, Robert Nelson, who wrote the well-known book on “Fasts and Festivals,” gave £100 in trust as the first legacy to the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. Mr. Noble quotes a curious broadside still extant in which the second Sir Richard Hoare, who died in 1754, denies a false and malicious report that he had attempted to cause a run on the Bank of England, and to occasion a disturbance in the City, by sending persons to the Bank with ten notes of £10 each. What a state of commercial wealth, to be shaken by the sudden demand of a mere £100!
Next to Hoare’s once stood the “Mitre Tavern,” where some of the most interesting of the meetings between Dr. Johnson and Boswell took place. The old tavern was pulled down, in 1829, by the Messrs. Hoare, to extend their banking-house. The original “Mitre” was of Shakespeare’s time. In some MS. poems by Richard Jackson, a contemporary of the great poet, are some verses beginning, “From the rich Lavinian shore,” inscribed as “Shakespeare’s rime, which he made at ye ‘Mitre,’ in Fleet Street.” The balcony was set on flames during the Great Fire, and had to be pulled down. Here, in June, 1763, Boswell came by solemn appointment to meet Johnson, so long the god of his idolatry. They had first met at the shop of Davis, the actor and bookseller, and afterwards near an eating-house in Butcher Row. Boswell describes his feelings with delightful sincerity and, self-complacency. “We had,” he says, “a good supper and port wine, of which Johnson then sometimes drank a bottle. The orthodox High Church sound of the Mitre, the figure and manner of the celebrated Samuel Johnson, the extraordinary power of his conversation, and the pride arising from finding myself admitted as his companion, produced a variety of sensations and a pleasing elevation of mind beyond what I had ever before experienced.” That memorable evening Johnson ridiculed Colley Cibber’s birthday odes and Paul Whitehead’s “grand nonsense,” and ran down Gray, who had declined his acquaintance. He talked of other poets, and praised poor Goldsmith as a worthy man and excellent author. Boswell fairly won the great man by his frank avowals and his adroit flattery. “Give me your hand,” at last cried the great man to the small man: “I have taken a liking to you.” They then finished a bottle of port each, and parted between one and two in the morning. As they shook hands, on their way to No. 1, Inner Temple Lane, where Johnson then lived, Johnson said, “Sir, I am glad we have met. I hope we shall pass many evenings, and mornings too, together.” A few weeks after the Doctor and his young disciple met again at the “Mitre,” and Goldsmith was present. The poet was full of love for Dr. Johnson, and speaking of some scapegrace, said tenderly, “He is now become miserable, and that insures the protection of Johnson.” At another “Mitre” meeting, on a Scotch gentleman present praising Scotch scenery, Johnson uttered his bitter gibe, “Sir, let me tell you that the noblest prospect which a Scotchman ever sees is the high road that leads him to England.” In the same month Johnson and Boswell met again at the “Mitre.” The latter confessed his nerves were much shaken by the old port and the late tavern hours; and Johnson laughed at people who had accepted a pension from the house of Hanover abusing him as a Jacobite. It was at the “Mitre” that Johnson urged Boswell to publish his “Travels in Corsica;” and at the “Mitre” he said finely of London, “Sir, the happiness of London is not to be conceived but by those who have been in it. I will venture to say there is more learning and science within the circumference of ten miles from where we sit than in all the rest of the kingdom.” It was here the famous “Tour to the Hebrides” was planned and laid out. Another time we find Goldsmith and Boswell going arm-in-arm to Bolt Court, to prevail on Johnson to go and sup at the “Mitre;” but he was indisposed. Goldsmith, since “the big man” could not go, would not venture at the “Mitre” with Boswell alone. At Boswell’s last “Mitre” evening with Johnson, May, 1778, Johnson would not leave Mrs. Williams, the blind old lady who lived with him, till he had promised to send her over some little dainty from the tavern. This was very kindly and worthy of the man who had the coat but not the heart of a bear. From 1728 to 1753 the Society of Antiquaries met at the “Mitre,” and discussed subjects then wrongly considered frivolous. The Royal Society had also conclaves at the same celebrated tavern; and here, in 1733, Thomas Topham, the strongest man of his day, in the presence of eight persons, rolled up with his iron fingers a large pewter dish. In 1788 the “Mitre” ceased to be a tavern, and became, first Macklin’s Poet’s Gallery, and then an auctionroom. The present spurious “Mitre Tavern,” in Mitre Court, was originally known as “Joe’s Coffee. House.”
It was at No. 56 (south side) that Lamb’s friend, William Hone, the publisher of the delightful “Table Book” and “Every-day Book,” commenced business about 1812. In 1815 he was brought before the Wardmote Inquest of St. Dunstan’s for placarding his shop on Sundays, and for carrying on a retail trade as bookseller and stationer, not being a freeman. The Government had no doubt suggested the persecution of so troublesome an opponent, whose defence of himself is said to have all but killed Lord Ellenborough, the judge who tried him for publishing blasphemous parodies. In 1815 Hone took great interest in the case of Eliza Fenning, a poor innocent servant girl, who was hung for a supposed attempt to poison her master, a law stationer in Chancery Lane. It was afterwards believed that a nephew of Mr. Turner really put the poison in the dough of some dumplings, in revenge at being kept short of money.
Mr. Cyrus Jay, a shrewd observer, was present at Hone’s trial, and has described it with vividness:—
“Hone defended himself firmly and well, but he had no spark of eloquence about him. For years afterwards I was often with him, and he was made a great deal of in society. He became very religious, and died a member of Mr. Clayton’s Independent chapel, worshipping at the Weigh House. The last important incident of Lord Ellenborough’s political life was the part he took as presiding judge in Hone’s trials for the publication of certain blasphemous parodies. At this time he was suffering from the most intense exhaustion, and his constitution was sinking under the fatigues of a long and sedulous discharge of his important duties. This did not deter him from taking his seat upon the bench on this occasion. When he entered the court, previous to the trial, Hone shouted out, ‘I am glad to see you, Lord Ellenborough. I know what you are come here for; I know what you want.’ ‘I am come to do justice,’ replied his lordship. ‘My wish is to see justice done.’ ‘Is it not rather, my lord,’ retorted Hone, ‘to send a poor devil of a bookseller to rot in a dungeon?’ In the course of the proceedings Lord Ellenborough more than once interfered. Hone, it must be acknowledged, with less vehemence than might have been expected, requested him to forbear. The next time his lordship made an observation, in answer to something the defendant urged in the course of his speech, Hone exclaimed, in a voice of thunder, ‘I do not speak to you, my lord; you are not my judge; these,’ pointing to the jury, ‘these are my judges, and it is to them that I address myself.’ Hone avenged himself on what he called the Chief Justice’s partiality; he wounded him where he could not defend himself. Arguing that Athanasius was not the author of the creed that bears his name, he cited, by way of authority, passages from the writings of Gibbon and Warburton to establish his position. Fixing his eyes on Lord Ellenborough, he then said, “And, further, your lordship’s father, the late worthy Bishop of Carlisle, has taken a similar view of the same creed.’ Lord Ellenborough could not endure this allusion to his father’s heterodoxy. In a broken voice he exclaimed, ‘For the sake of decency, forbear!’ The requestwas immediately complied with. The jury acquitted Hone, a result which is said to have killed the Chief Justice; but this is probably not true. That he suffered in consequence of the trial is certain. After he entered his private room, when the trial was over, his strength had so far deserted him that his son was obliged to put his hat on for him. But he quickly recovered his spirits; and on his way home, in passing through Charing Cross, he pulled the check-string, and said, ‘It just occurs to me that they sell here the best herrings in London; buy six.’ Indeed Dr. Turner, afterwards Bishop of Calcutta, who accompanied him in his carriage, said that so far from his nerves being shaken by the hootings of the mob, Lord Ellenborough only observed that their saliva was worse than their bite. . . . .
“When Hone was tried before him for blasphemy, Lord Tenterden treated him with great forbearance; but Hone, not content with the indulgence, took to vilifying the judge. ‘Even in a Turkish court I should not have met with the treatment I have experienced here,’ he exclaimed. ‘Certainly,’ replied Lord Tenterden; ‘the bowstring would have been round your neck an hour ago.”
That sturdy political writer, William Cobbett, lived at No. 183 (north), and there published his Political Register. In 1819 he wrote from America, declaring that if Sir Robert Peel’s Bank Bill passed, he would give Castlereagh leave to lay him on a gridiron and broil him alive, while Sidmouth stirred the coals, and Canning stood by and laughed at his groans. In 1827 he announced in his Register that he would place a gridiron on the front of his shop whenever Peel’s Bill was repealed. The “Small Note Bill” was repealed, when there was a reduction of the interest of the National Debt. The gridiron so often threatened never actually went up, but it was to be seen a few years ago nailed on the gable end of a candle manufacturer’s at Kensington. The two houses next to Cobbett’s (184 and 185) are the oldest houses standing in Fleet Street.
“Peele’s Coffee-House” (Nos. 177 and 178, north side) once boasted a portrait of Dr. Johnson, said to be by Sir Joshua Reynolds, on the keystone of the mantelpiece. This coffee-house is of antiquity, but is chiefly memorable for its useful files of newspapers and for its having been the central committee-room of the Society for Repealing the Paper Duty. The struggle began in 1858, and eventually triumphed, thanks to the president, the Right Hon. Milner Gibson, and the chairman, the late Mr. John Cassell. The house within the last few years has been entirely rebuilt. In former times “Peele’s Coffee-House” was quite a house of call and postoffice for money-lenders and bill-discounters; though crowds of barristers and solicitors also frequented it, in order to consult the useful files of London and country newspapers hoarded there for now more than a century. Mr. Jay has left us an amusing sketch of one of the former frequenters of “Peele’s”—the late Sir William Owen Barlow, a bencher of the Middle Temple. This methodical old gentleman had never travelled in a stage-coach or railway-carriage in his life, and had not for years read a book. He came in for dinner at the same hour every day, except in Term-time, and was very angry if any loud talkers disturbed him at his evening paper. He once requested the instant discharge of a waiter at “Peele’s,” because the civil but ungrammatical man had said, “There are a leg of mutton, and there is chops.”
The original “Green Dragon” (No. 56, south) was destroyed by the Great Fire, and the new building set six feet backward. During the Popish Plot several anti-papal clubs met here; and from the windows Roger North stood to see the shouting, torch-waving procession pass along, to burn the Pope’s effigy at Temple Bar. In the “Discussion Forum” many Lord Chancellors of the future have tried their eloquence. It was celebrated some years ago from an allusion to it made by Napoleon III.
At No. 67 (corner of Whitefriars Street) once lived that famous watchmaker of Queen Anne’s reign, Thomas Tompion, who is said, in 1700, to have begun a clock for St. Paul’s Cathedral which was to go one hundred years without winding up. He died in 1713. His apprentice, George Graham, invented, as Mr. Noble tells us, the horizontal escapement, in 1724. He was succeeded by Mudge and Dutton, who, in 1768, made Dr. Johnson his first watch. The old shop was (1850) one of the last in Fleet Street to be modernised.
Between Bolt and Johnson’s courts (152–166, north)—say near “Anderton’s Hotel”—there lived, in the reign of George II., at the sign of the “Astronomer’s Musical Clock,” Christopher Pinchbeck, an ingenious musical-clockmaker, who invented the “cheap and useful imitation of gold,” which still bears his name. (Watt’s, in his “Dictionary of Chemistry,” says “pinchbeck” is an alloy of copper and zinc, usually containing about nine parts copper to one part zinc. Brandt says it is an alloy containing more copper than exists in brass, and consequently made by fusing various proportions of copper with brass.) Pinchbeck often exhibited his musical automata in a booth at Bartholomew Fair, and, in conjunction with Fawkes the Conjuror, at Southwark Fair. He made, according to Mr. Wood, an exquisite musical clock, worth about £500, for Louis XIV., and a fine organ for the Great Mogul, valued at £300. He died in 1732. He removed to Fleet Street (between Bolt and Johnson’s courts, north side) from Clerkenwell in 1721. His clocks played tunes and imitated the notes of birds. In 1765 he set up, at the Queen’s House, a clock with four faces, showing the age of the moon, the day of the week and month, the time of sun rising, &c.
No. 161 (north) was the shop of Thomas Hardy, that agitating bootmaker, secretary to the London Corresponding Society, who was implicated in the John Horne Tooke trials of 1794; and next door, years after (No. 162), Richard Carlisle, a “freethinker,” opened a lecturing, conversation, and discussion establishment, preached the “only true gospel,” hung effigies of bishops outside his shop, and was eventually quieted by nine years’ imprisonment, a punishment by no means undeserved. No. 76 (south) was once the entrance to the printing-office of Samuel Richardson, the author of “Clarissa,” who afterwards lived in Salisbury Square, and there held levees of his admirers, to whom he read his works with an innocent vanity which occasionally met with disagreeable rebuffs.
“Anderton’s Hotel” (No. 164, north side) occupies the site of a house given, as Mr. Noble says, in 1405, to the Goldsmiths’ Company, under the singular title of “The Horn in the Hoop,” probably at that time a tavern. In the register of St. Dunstan’s is an entry (1597), “Ralph slaine at the Horne, buryed,” but no further record exists of this hot-headed roysterer. In the reign of King James I. the “Horn” is described as “between the ‘Red Lion,’ over against Serjeants’ Inn, and Three-legged Alley.”
The Record (No. 169, north side) started in 1828 as an organ of the extreme Evangelical party. The first promoters were the late Mr. James Evans, a brother of Sir Andrew Agnew, and Mr. Andrew Hamilton, of West Ham Common (the first secretary of the Alliance Insurance Company). Among their supporters were Henry Law, Dean of Gloucester, and Francis Close, afterwards Dean of Carlisle. Amongst its earliest writers was the celebrated Dr. John Henry Newman, of Oxford. The paper was all but dying when a new “whip” was made for money, and the Rev. Henry Blunt, of Chelsea, became for a short time its editor. The Record at last began to flourish and to assume a bolder and a more independent tone. Dean Milman’s neology, the peculiarities of the Irvingites, and the dangerous Oxford tracts, were alternately denounced. In due course the Record began to appear three times a week, and became celebrated for its uncompromising religious tone and, as Mr. James Grant truly says, for the earliness and accuracy of its politico-ecclesiastical information.
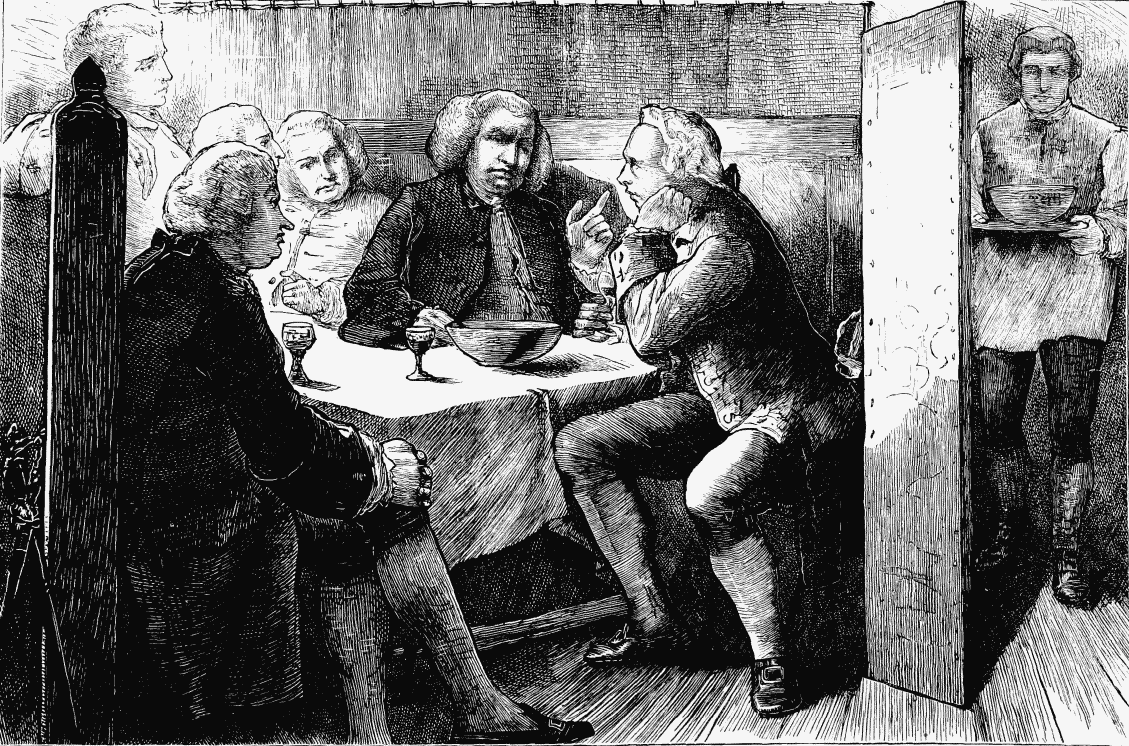
AN EVENING WITH DR. JOHNSON AT THE “MITRE.” (see page 51).
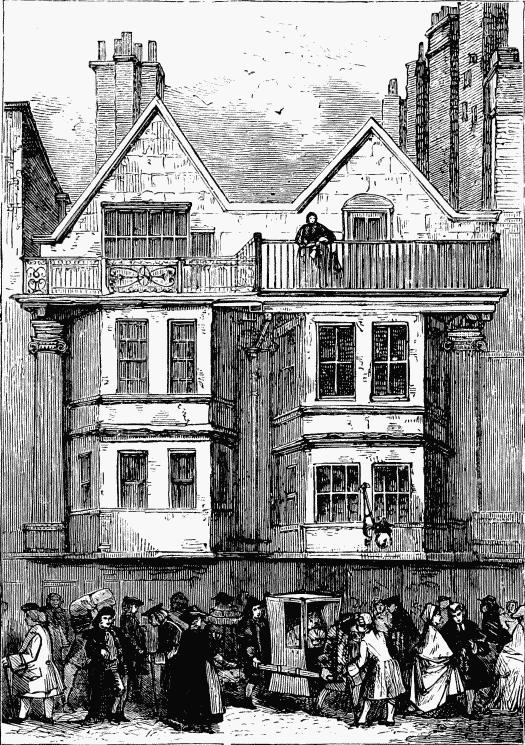
OLD HOUSES (STILL STANDING) IN FLEET STREET, NEAR ST. DUNSTAN’S CHURCH (see page 52).
The old church of St. Bride (Bridget) was of great antiquity. As early as 1235 we find a turbulent foreigner, named Henry de Battle, after slaying one Thomas de Hall on the king’s highway, flying for sanctuary to St. Bride’s, where he was guarded by the aldermen and sheriffs, and examined in the church by the Constable of the Tower. The murderer, after confessing his crime, abjured the realm. In 1413 a priest of St. Bride’s was hung for an intrigue in which he had been detected. William Venor, a warden of the Fleet Prison, added a body and side-aisles in 1480 (Edward IV.) At the Reformation there were orchards between the parsonage gardens and the Thames. In 1637, a document in the Record Office, quoted by Mr. Noble, mentions that Mr. Palmer, vicar of St. Bride’s, at the service at seven a.m., sometimes omitted the prayer for the bishop, and, being generally lax as to forms, often read service without surplice, gown, or even his cloak. This worthy man, whose living was sequestered in 1642, is recorded, in order to save money for the poor, to have lived in a bed-chamber in St. Bride’s steeple. He founded an almshouse in Westminster, upon which Fuller remarks, in his quaint way, “It giveth the best light when one carrieth his lantern before him.” The brother of Pepys was buried here in 1664 under his mother’s pew. The old church was swallowed up by the Great Fire, and the present building erected in 1680, at a cost of £11,430 5s. IId. The tower and spire were considered master-pieces of Wren. The spire, originally 234 feet high, was struck by lightning in 1754, and it is now only 226 feet high. It was again struck in 1803. The illuminated dial (the second erected in London) was set up permanently in 1827. The Spital sermons, now preached in Christ Church, Newgate Street, were preached in St. Bride’s from the Restoration till 1797. They were originally all preached in the yard of the hospital of St. Mary Spital, Bishopsgate. Mr. Noble, has ransacked the records relating to St. Bride’s with the patience of old Stow. St. Bride’s, he says, was renowned for its tithe-rate contests; but after many lawsuits and great expense, a final settlement of the question was come to in the years 1705–6. An Act was passed in 1706, by which Thomas Townley, who had rented the tithes for twenty-one years, was to be paid £1,200 within two years, by quarterly payments and £400 a year afterwards. In 1869 the inappropriate rectory of St. Bridget and the tithes thereof, except the advowson, the parsonage house, and Easter-dues offerings, were sold by auction for £2,700. It may be here worthy to note, says Mr. Noble, that in 1705 the number of rateable houses in the parish of St. Bride was 1,016, and the rental, £18,374; in 1868 the rental was £205,407 gross, or £168,996 rateable.
Mr. Noble also records pleasantly the musical feats accomplished on the bells of St. Bride’s. In 1710 ten bells were cast for this church by Abraham Rudhall, of Gloucester, and on the 11th of January, 1717, it is recorded that the first complete peal of 5,040 grandsire caters ever rung was effected by the “London scholars.” In 1718 two treble bells were added; and on the 9th of January, 1724, the first peal ever completed in this kingdom upon twelve bells was rung by the college youths; and in 1726 the first peal of Bob Maximus, one of the ringers being Mr. Francis (afterwards Admiral) Geary. It was reported by the ancient ringers, says our trustworthy authority, that every one who rang in the last-mentioned peal left the church in his own carriage. Such was the dignity of the “campanularian” art in those days. When St. Bride’s bells were first put up, Fleet Street used to be thronged with carriages full of gentry, who had come far and near to hear the pleasant music float aloft. During the terrible Gordon Riots, in 1780, Brasbridge, the silversmith, who wrote an autobiography, says he went up to the top of St. Bride’s steeple to see the awful spectacle of the conflagration of the Fleet Prison, but the flakes of fire, even at that great height, fell so thickly as to render the situation untenable.
Many great people lie in and around St. Bride’s; and Mr. Noble gives several curious extracts from the registers. Among the names we find Wynkyn de Worde, the second printer in London; Baker, the chronicler; Lovelace, the Cavalier poet, who died of want in Gunpowder Alley, Shoe Lane; Ogilby, the translator of Homer; the Countess of Orrery (1710); Elizabeth Thomas, a lady immortalised by Pope; and John Hardham, the Fleet Street tobacconist. The entrance to the vault of Mr. Holden (a friend of Pepys), on the north side of the church, is a relic of the older building. Inside St. Bride’s are monuments to Richardson, the novelist; Nichols, the historian of Leicestershire; and Alderman Waithman. Among the clergy of St. Bride’s Mr. Noble notes John Cardmaker, who was burnt at Smithfield for heresy, in 1555; Fuller, the Church historian and author of the “Worthies,” who was lecturer here; Dr. Isaac Madox, originally an apprentice to a pastrycook, and who died Bishop of Winchester in 1759; and Dr. John Thomas, vicar, who died in 1793. There were two John Thomases among the City clergy of that time. They were both chaplains to the king, both good preachers, both. squinted, and both died bishops!
The present approach to St. Bride’s, designed by J. P. Papworth, in 1824, cost £10,000, and was urged forward by Mr. Blades, a Tory tradesman of Ludgate Hill, and a great opponent of Alderman Waithman. A fire that had destroyed some ricketty old houses gave the requisite opportunity for letting air and light round poor, smothered-up St. Bride’s.
The office of Punch (No. 85, south side) is said to occupy the site of the small school, in the house of a tailor, in which Milton once earned a precarious living. Here, ever since 1841, the pleasant jester of Fleet Street has scared folly by the jangle of his bells and the blows of his staff. The best and most authentic account of the origin of Punch is to be found in the following communication to Notes and Queries, September 30, 1870. Mr. W. H. Wills, who was one of the earliest contributors to Punch, says:—
“The idea of converting Punch from a strolling to a literary laughing philosopher belongs to Mr. Henry Mayhew, former editor (with his schoolfellow Mr. Gilbert à Beckett) of Figaro in London. The first three numbers, issued in July and August, 1841, were composed almost entirely by that gentleman, Mr. Mark Lemon, Mr. Henry Plunkett (‘Fusbos’), Mr. Stirling Coyne, and the writer of these lines. Messrs. Mayhew and Lemon put the numbers together, but did not formally dub themselves editors until the appearance of their ‘Shilling’s Worth of Nonsense.’ The cartoons, then ‘Punch’s Pencillings,’ and the smaller cuts, were drawn by Mr. A. S. Henning, Mr. Newman, and Mr. Alfred Forester (‘Crowquill’); later, by Mr. Hablot Browne and Mr. Kenny Meadows. The designs were engraved by Mr. Ebenezer Landells, who occupied also the important position of ‘capitalist.’ Mr. Gilbert à Beckett’s first contribution to Punch, ‘The Abovebridge Navy,’ appeared in No. 4, with Mr. John Leech’s earliest cartoon, ‘Foreign Affairs.’ It was not till Mr. Leech’s strong objection to treat political subjects was overcome, that, long after, he began to illustrate Punch’s pages regularly. This he did, with the brilliant results that made his name famous, down to his untimely death. The letterpress description of ‘Foreign Affairs’ was written by Mr. Percival Leigh, who—also after an interval—steadily contributed. Mr. Douglas Jerrold began to wield Punch’s baton in No. 9. His ‘Peel Regularly Called in’ was the first of those withering political satires, signed with a ‘J’ in the corner of each page opposite to the cartoon, that conferred on Punch a wholesome influence in politics. Mr. Albert Smith made his début in this wise:—At the birth of Punch had just died a periodical called (I think) the Cosmorama. When moribund, Mr. Henry Mayhew was called in to resuscitate it. This periodical bequeathed a comic census-paper filled up, in the character of a showman, so cleverly that the author was eagerly sought at the starting of Punch. He proved to be a medical student hailing from Chertsey, and signing the initials A. S.—only,’ remarked Jerrold, ‘twothirds of the truth, perhaps.’ This pleasant supposition was, however, reversed at the very first introduction. On that occasion Mr. Albert Smith left the ‘copy’ of the opening of ‘The Physiology of the London Medical Student.’ The writers already named, with a few volunteers selected from the editor’s box, filled the first volume, and belonged to the ante-‘B. & E.’ era of Punch’shistory. The proprietary had hitherto consisted of Messrs. Henry Mayhew, Lemon, Coyne, and Landells. The printer and publisher also held shares, and were treasurers. Although the popularity of Punch exceeded all expectation, the first volume ended in difficulties. From these storm-tossed seas Punch was rescued and brought into smooth water by Messrs. Bradbury & Evans, who acquired the copyright and organised the staff. Then it was that Mr. Mark Lemon was appointed sole editor, a new office having been created for Mr. Henry Mayhew—that of Suggestor-in-Chief; Mr. Mayhew’s contributions, and his felicity in inventing pictorial and in ‘putting’ verbal witticisms, having already set a deep mark upon Punch’s success. The second volume started merrily. Mr. John Oxenford contributed his first jeu d’esprit in its final number on ‘Herr Döbler and the Candle-Counter.’ Mr. Thackeray commenced his connection in the beginning of the third volume with ‘Miss Tickletoby’s Lectures on English History,’ illustrated by himself. A few weeks later a handsome young student returned from Germany. He was heartily welcomed by his brother, Mr. Henry Mayhew, and then by the rest of the fraternity. Mr. Horace Mayhew’s diploma joke consisted, I believe, of ‘Questions addressées au Grand Concours aux Elèves d’Anglais du Collége St. Badaud, dans le Département de la Haute Cockaigne’ (vol. iii., p. 89). Mr. Richard Doyle, Mr. Tenniel, Mr. Shirley Brooks, Mr. Tom Taylor, and the younger celebrities who now keep Mr. Punch in vigorous and jovial vitality, joined his establishment after some of the birth-mates had been drafted off to graver literary and other tasks.”
Mr. Mark Lemon remained editor of Punch from 1841 till 1870, when he died. Mr. Gilbert à Beckett died at Boulogne in 1856. This most accomplished and gifted writer succeeded in the more varied kinds of composition, turning with extraordinary rapidity from a Times leader to a Punch epigram.
A pamphlet attributed to Mr. Blanchard conveys, after all, the most minute account of the origin of Punch. A favourite story of the literary gossipers who have made Mr. Punch their subject from time to time, says the writer, is that he was born in a tavern parlour. The idea usually presented to the public is, that a little society of great men used to meet together in a private room in a tavern close to Drury Lane Theatre—the “Crown Tàvern,” in Vinegar Yard. The truth is this:—
In the year 1841 there was a printing-office in a court running out of Fleet Street—No. 3, Crane Court—wherein was carried on the business of Mr. William Last. It was here that Punch first saw the light. The house, by the way, enjoys besides a distinction of a different kind—that of being the birthplace of “Parr’s Life Pills;” for Mr. Herbert Ingram, who had not at that time launched the Illustrated London News, nor become a member of Parliament, was then introducing that since celebrated medicine to the public, and for that purpose had rented some rooms on the premises of his friend Mr. Last.
The circumstance which led to Punch’s birth was simple enough. In June, 1841, Mr. Last called upon Mr. Alfred Mayhew, then in the office of his father, Mr. Joshua Mayhew, the well-known solicitor, of Carey Street, Lincoln’s Inn Fields. Mr. Mayhew was Mr. Last’s legal adviser, and Mr. Last was well acquainted with several of his sons. Upon the occasion in question Mr. Last made some inquiries of Mr. Alfred Mayhew concerning his brother Henry, and his occupation at the time. Mr. Henry Mayhew had, even at his then early age, a reputation for the high abilities which he afterwards developed, had already experience in various departments of literature, and had exercised his projective and inventive faculties in various ways. If his friends had heard nothing of him for a few months, they usually found that he had a new design in hand, which was, however, in many cases, of a more original than practical character. Mr. Henry Mayhew, as it appeared from his brother Alfred’s reply, was not at that time engaged in any new effort of his creative genius, and would be open to a proposal for active service.
Having obtained Mr. Henry Mayhew’s address, which was in Clement’s Inn, Mr. Last called upon that gentleman on the following morning, and opened to him a proposal for a comic and satirical journal. Henry Mayhew readily entertained the idea; and the next question was, “Can you get up a staff?” Henry Mayhew mentioned his friend Mark Lemon as a good commencement; and the pair proceeded to call upon that gentleman, who was living, not far off, in Newcastle Street, Strand. The almost immediate result was the starting of Punch.
At a meeting at the “Edinburgh Castle” Mr. Mark Lemon drew up the original prospectus. It was at first intended to call the new publication “The Funny Dog,” or “Funny Dog, with Comic Tales,” and from the first the subsidiary title of the “London Charivari” was agreed upon. At a subsequent meeting at the printing-office, some one made some allusion to the “Punch,” and some joke about the “Lemon” in it. Henry Mayhew, with his usual electric quickness, at once flew at the idea, and cried out, “A good thought; we’ll call it Punch.” It was then remembered that, years before, Douglas Jerrold had edited a Penny Punch for Mr. Duncombe, of Middle Row, Holborn, but this was thought no objection, and the new name was carried by acclamation. It was agreed that there should be four proprietors—Messrs. Last, Landells, Lemon, and Mayhew. Last was to supply the printing, Landells the engraving, and Lemon and Mayhew were to be co-editors. George Hodder, with his usual good-nature, at once secured Mr. Percival Leigh as a contributor, and Leigh brought in his friend Mr. John Leech, and Leech brought in Albert Smith. Mr. Henning designed the cover. When Last had sunk £600, he sold it to Bradbury & Evans, on receiving the amount of his then outstanding liabilities. At the transfer, Henning and Newman both retired, Mr. Coyne and Mr. Grattan seldom contributed, and Messrs. Mayhew and Landells also seceded.
Mr. Hine, the artist, remained with Punch for many years; and among other artistic contributors who “came and went,” to use Mr. Blanchard’s own words, we must mention Birket Foster, Alfred Crowquill, Lee, Hamerton, John Gilbert, William Harvey, and Kenny Meadows, the last of whom illustrated one of Jerrold’s earliest series, “Punch’s Letters to His Son.” Punch’s Almanac for 1841 was concocted for the greater part by Dr. Maginn, who was then in the Fleet Prison, where Thackeray has drawn him, in the character of Captain Shandon, writing the famous prospectus for the Pall Mall Gasetle. The earliest hits of Punch were Douglas Jerrold’s articles signed “J.” and Gilbert à Beckett’s “Adventures of Mr. Briefless.” In October, 1841, Mr. W. H. Wills, afterwards working editor of Household Words and All the Year Round, commenced “Punch’s Guide to the Watering-Places.” In January, 1842, Albert Smith commenced his lively “Physiology of London Evening Parties,” which were illustrated by Newman; and he wrote the “Physiology of the London Idler,” which Leech illustrated. In the third volume, Jerrold commenced “Punch’s Letters to His Son;” and in the fourth volume, his “Story of a Feather;” Albert Smith’s “Side-Scenes of Society” carried on the social dissections of the comic physiologist, and à Beckett began his “Heathen Mythology,” and created the character of “Jenkins,” the supposed fashionable correspondent of the Morning Post. Punch had begun his career by ridiculing Lord Melbourne; he now attacked Brougham, for his temporary subservience to Wellington; and Sir James Graham came also in for a share of the rod; and the Morning Herald and Standard were christened “Mrs. Gamp” and “Mrs. Harris,” as oldfogyish opponents of Peel and the Free-Traders. À Beckett’s “Comic Blackstone” proved a great hit, from its daring originality; and incessant jokes were squibbed off on Lord John Russell, Prince Albert (for his military tailoring), Mr. Silk Buckingham and Lord William Lennox, Mr. Samuel Carter Hall and Mr. Harrison Ainsworth. Tennyson once, and once only, wrote for Punch, a reply to Lord Lytton (then Mr. Bulwer), who had coarsely attacked him in his “New Timon,” where he had spoken flippantly of.
“A quaint farrago of absurd conceits,
Out-babying Wordsworth and out-glittering Keats.”
The epigram ended with these bitter and contemptuous lines,—
“A Timon you? Nay, nay, for shame!
It looks too arrogant a jest—
That fierce old man—to take his name,
You bandbox! Off, and let him rest.”
Albert Smith left Punch many years before his death. In 1845, on his return from the East, Mr. Thackeray began his “Jeames’s Diary,” and became a regular contributor. Gilbert à Beckett was now beginning his “Comic History of England” and Douglas Jerrold his inimitable “Caudle Lectures.” Thomas Hood occasionally contributed, but his immortal “Song of the Shirt” was his chef-d’ œuvre. Coventry Patmore contributed once to Punch; his verses denounced General Pellisier and his cruelty at the caves of Dahra. Laman Blanchard occasionally wrote; his best poem was one on the marriage and temporary retirement of charming Mrs. Nisbett. In 1846 Thackeray’s “Snobs of England” was highly successful. Richard Doyle’s “Manners and Customs of ye English” brought Punch much increase. The present cover of Punch is by Doyle, who, being a zealous Roman Catholic, eventually left Punchwhen it began to ridicule the Pope and condemn Papal aggression. Punch in his time has had his raps, but not many and not hard ones. Poor Angus B. Reach (whose mind went early in life), with Albert Smith and Shirley Brooks, ridiculed Punch in the Man in the Moon, and in 1847 the Poet Bunn—”Hot, cross Bunn”—provoked at incessant attacks on his operatic verses, hired a man of letters to write “A Word with Punch,” and a few smart personalities soon silenced the jester. “Towards 1848,” says Mr. Blanchard, “Douglas Jerrold, then writing plays and editing a magazine, began to write less for Punch.” In 1857 he died. Among the later additions to the staff were Mr. Tom Taylor and Mr. Shirley Brooks.
The Dispatch (No. 139, north) was established by Mr. Bell, in 1801. Moving from Bride Lane to Newcastle Street, and thence to Wine Office Court, it settled down in the present locality in 1824. Mr. Bell was an energetic man, and the paper succeeded in obtaining a good position; but he was not a man of large capital, and other persons had shares in the property. In consequence of difficulties between the proprietors there were at one time three Dispatches in the field— Bell’s, Kent’s, and Duckett’s; but the two lastmentioned were short-lived, and Mr. Bell maintained his position. Bell’s was a sporting paper, with many columns devoted to pugilism, and a woodcut exhibiting two boxers ready for an encounter. But the editor (says a story more or less authentic), Mr. Samuel Smith, who had obtained his post by cleverly reporting a fight near Canterbury, one day received a severe thrashing from a famous member of the ring. This changed the editor’s opinions as to the propriety of boxing— at anyrate pugilism was repudiated by the Dispatch about 1829; and boxing, from the Dispatch point of view, was henceforward treated as a degrading and brutal amusement, unworthy of our civilisation.
Mr. Harmer (afterwards Alderman), a solicitor in extensive practice in Old Bailey cases, became connected with the paper about the time when the Fleet Street office was established, and contributed capital, which soon bore fruit. The success was so great, that for many years the Dispatch as a property was inferior only to the Times. It became famous for its letters on political subjects. The original “Publicola” was Mr. Williams, a violent and coarse but very vigorous and popular writer. He wrote weekly for about sixteen or seventeen years, and after his death the signature was assumed by Mr. Fox, the famous orator and member for Oldham. Other writers also borrowed the well-known signature. Eliza Cooke wrote in the Dispatch in 1836, at first signing her poems “E.” and “E. C.”; but in the course of the following year her name appeared in full. She contributed a poem weekly for several years, relinquishing her connection with the paper in 1850. Afterwards, in 1869,. when the property changed hands, she wrote two or three poems. Under the signature “Caustic,” Mr. Serle, the dramatic author and editor, contributed a weekly letter for about twenty-seven years; and from 1856 till 1869 was editor-in-chief. In 1841–42 the Dispatch had a hard-fought duel with the Times. “Publicola” wrote a series of letters, which had the effect of preventing the election of Mr. Walter for Southwark. The Times retaliated when the time came for Alderman Harmer to succeed to the lord mayoralty. Day after day the Times returned to the attack, denouncing the Dispatch as an infidel paper; and Alderman Harmer, rejected by the City, resigned in consequence his aldermanic gown. In 1857 the Dispatch commenced the publication of its famous “Atlas,” giving away a good map weekly for about five years. The price was reduced from fivepence to twopence, at the beginning of 1869, and to a penny in 1870.
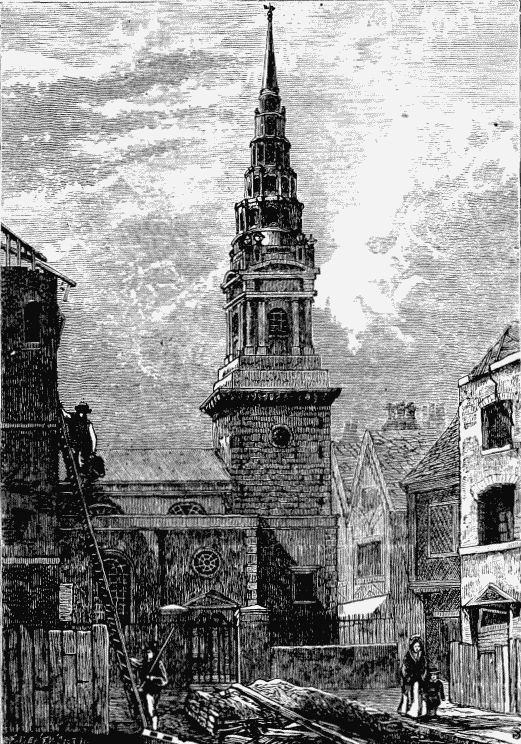
ST. BRIDE’S CHURCH, FLEET STREET, AFTER THE FIRE, 1824 (see page 56).
The Daily Telegraph office is No. 136 (north). Mr. Ingram, of the Illustrated London News, originated a paper called the Telegraph, which lasted only seven or eight weeks. The present Daily Telegraph was started on June 29, 1855, by the late Colonel Sleigh. It was a single sheet, and the price twopence. Colonel Sleigh failing to make it a success, Mr. Levy, the present chief proprietor of the paper, took the copyright as part security for money owed him by Colonel Sleigh, In Mr. Levy’s hands the paper, reduced to a penny, became a great success. “It was,” says Mr. Grant, in his “History of the Newspaper Press,” “the first of the penny papers, while a single sheet, and as such was regarded as a newspaper marvel; but when it came out—which it did soon, after the Standard—as a double sheet the size of the Times, published at fourpence, for a penny, it created quite a sensation. Here was a penny paper, containing not only the same amount of telegraphic and general information as the other high-priced papers—their price being then fourpence—but also evidently written, in its leading article department, with an ability which, could only be surpassed by that of the leading articles of the Times itself. This was indeed a new era in the morning journalism of the metropolis.” When Mr. Levy bought the Telegraph, the sum which he received for advertisements in the first number was exactly 7s. 6d. The daily receipts for advertisements are now said to exceed £500. Mr. Grant says that the remission of the tax on paper brought £12,000 a year extra to the Telegraph. Ten pages for a penny is no uncommon thing with the Telegraph during the Parliamentary session. The returns of sales given by the Telegraphfor the half-year ending 1870 show an average daily sale of 190,885; and though this was war time, a competent authority estimates the average daily sale at 175,000 copies. One of the printingmachines recently set up by the proprietors of the Telegraph throws off upwards of 200 copies per minute, or 12,000 an hour.

WAITHMAN’S SHOP (see page 60).
The “Globe Tavern” (No. 134, north), though now only a memory, abounds with traditions of Goldsmith and his motley friends. The house, in 1649, was leased to one Henry Hottersall for forty-one years, at the yearly rent of £75, ten gallons of Canary sack, and £400 fine. Mr. John Forster gives a delightful sketch of Goldsmith’s Wednesday evening club at the “Globe,” in 1767. When not at Johnson’s great club, Oliver beguiled his cares at a shilling rubber club at the “Devil Tavern,” or at a humble gathering in the parlour of the “Bedford,” Covent Garden. A hanger-on of the theatres, who frequented the “Globe,” has left notes which Mr. Forster has admirably used, and which we now abridge without further apology. Grim old Macklin belonged to the club it is certain; and among the less obscure members was King, the comedian, the celebrated impersonator of Lord Ogleby. Hugh Kelly, another member, was a clever young Irishman, who had chambers near Goldsmith in the Temple. He had been a staymaker’s apprentice, who, turning law writer, and soon landing as a hack for the magazines, set up as a satirist for the stage, and eventually, through Garrick’s patronage, succeeded in sentimental comedy. It was of him Johnson said, “Sir, I never desire to converse with a man who has written more than he has read.” Poor Kelly afterwards went to the Bar, and died of disappointment and over-work. A third member was Captain Thompson, a friend of Garrick’s, who wrote some good sea songs and edited “Andrew Marvell;” but foremost among all the boon companions was a needy Irish doctor named Glover, who had appeared on the stage, and who was said to have restored to life a man who had been hung; this Glover, who was famous for his songs and imitations, once had the impudence, like Theodore Hook, to introduce Goldsmith, during a summer ramble in Hampstead, to a party where he was an entire stranger, and to pass himself off as a friend of the host. “Our Dr. Glover,” says Goldsmith, “had a constant levee of his distressed countrymen, whose wants, as far as he was able, he always relieved.” Gordon, the fattest man in the club, was renowned for his jovial song of “Nottingham Ale;” and on special occasions Goldsmith himself would sing his favourite nonsense about the little old woman who was tossed seventeen times higher than the moon. A fat pork-butcher at the “Globe” used to offend Goldsmith by constantly shouting out, “Come, Noll, here’s my service to you, old boy.” After the success of The Goodnatured Man, this coarse familiarity was more than Goldsmith’s vanity could bear, so one special night he addressed the butcher with grave reproof. The stolid man, taking no notice, replied briskly, “Thankee, Mister Noll.” “Well, where is the advantage of your reproof?” asked Glover. “In truth,” said Goldsmith, good-naturedly, “I give it up; I ought to have known before that there is no putting a pig in the right way.” Sometimes rather cruel tricks were played on the credulous poet. One evening Goldsmith came in clamorous for his supper, and ordered chops. Directly the supper came in, the wags, by pre-agreement, began to sniff and swear. Some pushed the plate away; others declared the rascal who had dared set such chops before a gentleman should be made to swallow them himself. The waiter was savagely rung up, and forced to eat the supper, to which he consented with well-feigned reluctance, the poet calmly ordering a fresh supper and a dram for the poor waiter, “who otherwise might get sick from so nauseating a meal.” Poor Goldy! kindly even at his most foolish moments. A sadder story still connects Goldsmith with the “Globe.” Ned Purdon, a worn-out booksellers’ hack and a protégé of Goldsmith’s, dropped down dead in Smithfield. Goldsmith wrote his epitaph as he came from his chambers in the Temple to the “Globe.” The lines are:—
“Here lies poor Ned Purdon, from misery freed,
Who long was a booksellers’ hack;
He led such a miserable life in this world,
I don’t think he’ll wish to come back.”
Goldsmith sat next Glover that night at the club, and Glover heard the poet repeat, sotto voce, with a mournful intonation, the words,—
“I don’t think he’ll wish to come back.”
Oliver was musing over his own life, and Mr. Forster says touchingly, “It is not without a certain pathos to me, indeed, that he should have so repeated it.”
Among other frequenters of the “Globe” were Boswell’s friend Akerman, the keeper of Newgate, who always thought it prudent never to return home till daybreak; and William Woodfall, the celebrated Parliamentary reporter. In later times Brasbridge, the sporting silversmith of Fleet Street, was a frequenter of the club. He tells us that among his associates was a surgeon, who, living on the Surrey side of the Thames, had to take a boat every night (Blackfriar’s Bridge not being then built). This nightly navigation cost him three or four shillings a time, yet, when the bridge came, he grumbled at having to pay a penny toll. Among other frequenters of the “Globe,” Mr. Timbs enumerates “Archibald Hamilton, whose mind was ‘fit for a lord chancellor;’ Dunstall, the comedian; Carnan, the bookseller, who defeated the Stationers’ Company in the almanack trial; and, later still, the eccentric Hugh Evelyn, who set up a claim upon the great Surrey estate of Sir Frederic Evelyn.”
The Standard (No. 129, north), “the largest daily paper,” was originally an evening paper alone. In 1826 a deputation of the leading men opposed to Catholic Emancipation waited on Mr. Charles Baldwin, proprietor of the St. James’s Chronicle, and begged him to start an anti-Catholic evening paper, but Mr. Baldwin refused unless a preliminary sum of £15,000 was lodged at the banker’s. A year later this sum was deposited, and in 1827 the Evening Standard, edited by Dr. Giffard, ex-editor of the St. James’s Chronicle, appeared. Mr. Alaric Watts, the poet, was succeeded as sub-editor of the Standard by the celebrated Dr. Maginn. The daily circulation soon rose from 700 or 800 copies to 3,000 and over. The profits Mr. Grant calculates at £7,000 to £8,000 a year. On the bankruptcy of Mr. Charles Baldwin, Mr. James Johnson bought the Morning Herald and Standard, plant and all, for £16,500. The new proprietor reduced the Standard from fourpence to twopence, and made it a morning as well as an evening paper. In 1858 he reduced it to a penny only. The result was a great success. The annual income of the Standard is now, Mr. Grant says, “much exceeding yearly the annual incomes of most of the ducal dignities of the land.” The legend of the Duke of Newcastle presenting Dr. Giffard, in 1827, with £1,200 for a violent article against Roman Catholic claims, has been denied by Dr. Giffard’s son in the Times. The Duke of Wellington once wrote to Dr. Giffard to dictate the line the Standard and Morning Herald were to adopt on a certain question during the agitation on the Maynooth Bill; and Dr. Giffard withdrew his opposition to please Sir Robert Peel—a concession which injured the Standard. Yet in the following year, when Sir Robert Peel brought in his Bill for the abolition of the corn laws, he did not even pay Dr. Giffard the compliment of apprising him of his intention. Such is official gratitude when a tool is done with.
Near Shoe Lane lived one of Caxton’s disciples. Wynkyn de Worde, who is supposed to have been one of Caxton’s assistants or workmen, was a native of Lorraine. He carried on a prosperous career, says Dibdin, from 1502 to 1534, at the sign of the “Sun,” in the parish of St. Bride’s, Fleet Street. In upwards of four hundred works published by this industrious man he displayed unprecedented skill, elegance, and care, and his Gothic type was considered a pattern for his successors. The books that came from his press were chiefly grammars, romances, legends of the saints, and fugitive poems; he never ventured on an English New Testament, nor was any drama published bearing his name. His great patroness, Margaret, the mother of Henry VII., seems to have had little taste to guide De Worde in his selection, for he never reprinted the works of Chaucer or of Gower; nor did his humble patron, Robert Thorney, the mercer, lead him in a better direction. De Worde filled his blackletter books with rude engravings, which he used so indiscriminately that the same cut often served for books of a totally opposite character. By some writers De Worde is considered to be the first introducer of Roman letters into this country; but the honour of that mode of printing is now generally claimed by Pynson, a contemporary. Among other works published by De Worde were “The Ship of Fools,” that great satire that was so long popular in England; Mandeville’s lying “Travels;” “La Morte d’Arthur” (from which Tennyson has derived so much inspiration); “The Golden Legend;” and those curious treatises on “Hunting, Hawking, and Fishing,” partly written by yohanna Berners, a prioress of St. Alban’s. In De Worde’s “Collection of Christmas Carols” we find the words of that fine old song, still sung actually at Queen’s College, Oxford,—
“The boar’s head in hand bring I,
With garlands gay and rosemary.”
De Worde also published some writings of Erasmus. The old printer was buried in the parish church of St. Bride’s, before the high altar of St. Katherine; and he left land to the parish so that masses should be said for his soul. To his servants, not forgetting his bookbinder, Nowel, in Shoe Lane, he bequeathed books. De Worde lived near the Conduit, a little west of Shoe Lane. This conduit, which was begun in the year 1439 by Sir William Estfielde, a former Lord Mayor, and finished in 1471, was, according to Stow’s account, a stone tower, with images of St. Christopher on the top and angels, who, on sweet-sounding bells, hourly chimed a hymn with hammers, thus anticipating the wonders of St. Dunstan’s. These London conduits were great resorts for the apprentices, whom their masters sent with big leather and metal jugs to bring home the daily supply of water. Here these noisy, quarrelsome young rascals stayed to gossip, idle, and fight. At the coronation of Anne Boleyn this conduit was newly painted, all the arms and angels refreshed, and “the music melodiously sounding.” Upon the conduit was raised a tower with four turrets, and in every turret stood one of the cardinal virtues, promising never to leave the queen, while, to the delight and wonder of thirsty citizens, the taps ran with claret and red wine. Fleet Street, according to Mr. Noble, was supplied with water in the Middle Ages from the conduit at Marylebone and the holy wells of St. Clement’s and St. Bridget’s. The tradition is that the latter well was drained dry for the supply of the coronation banquet of George IV. As early as 1358 the inhabitants of Fleet Street complained of aqueduct pipes bursting and flooding their cellars, upon which they were allowed the privilege of erecting a pent-house over an aqueduct opposite the tavern of John Walworth, and near the house of the Bishop of Salisbury. In 1478 a Fleet Street wax-chandler, having been detected tapping the conduit pipes for his own use, was sentenced to ride through the City with a vessel shaped like a conduit on his felonious head, and the City crier walking before him to proclaim his offence.
The “Castle Tavern,” mentioned as early as 1432, stood at the south-west corner of Shoe Lane. Here the Clockmakers’ Company held their meetings before the Great Fire, and in 1708 the “Castle” possessed the largest sign in London. Early in the last century, says Mr. Noble, its proprietor was Alderman Sir John Task, a wine merchant, who died in 1735 (George II.), worth, it was understood, a quarter of a million of money.
The Morning Advertiser (No. 127, north) was established in 1794, by the Society of Licensed Victuallers, on the mutual benefit society principle. Every member is bound to take in the paper and is entitled to a share in its profits. Members unsuccessful in business become pensioners on the funds of the institution. The paper, which took the place of the Daily Advertiser, and was the suggestion of Mr. Grant, a master printer, was an immediate success. Down to 1850 the Morning Advertiser circulated chiefly in public-houses and coffee-houses at the rate of nearly 5,000 copies a day. But in 1850, the circulation beginning to decline, the committee resolved to enlarge the paper to the size of the Times, and Mr. James Grant was appointed editor. The profits now increased, and the paper found its way to the clubs. The late Lord Brougham and Sir David Brewster contributed to the Advertiser; and the letters signed “An Englishman” excited much interest. This paper has always been Liberal. Mr. Grant remained the editor for twenty years.
No. 91 (south side) was till lately the office of that old-established paper, Bell’s Weekly Messenger. Mr. Bell, the spirited publisher who founded this paper, is delightfully sketched by Leigh Hunt in his autobiography.
“About the period of my writing the above essays,” he says, in his easy manner, “circumstances introduced me to the acquaintance of Mr. Bell, the proprietor of the Weekly Messenger. In his house, in the Strand, I used to hear of politics and dramatic criticisms, and of the persons who wrote them. Mr. Bell had been well known as a bookseller and a speculator in elegant typography. It is to him the public are indebted for the small editions of the poets that preceded Cooke’s. Bell was, upon the whole, a remarkable person. He was a plain man, with a red face and a nose exaggerated by intemperance; and yet there was something not unpleasing in his countenance, especially when he spoke. He had sparkling black eyes, a good-natured smile, gentlemanly manners, and one of the most agreeable voices I ever heard. He had no acquirements—perhaps not even grammar; but his taste in putting forth a publication and getting the best artists to adorn it was new in those times, and may be admired in any. Unfortunately for Mr. Bell, the Prince of Wales, to whom he was bookseller, once did him the honour to partake of an entertainment or refreshment (I forget which—most probably the latter) at his house. He afterwards became a bankrupt. After his bankruptcy he set up a newspaper, which became profitable to everybody but himself.” (fn. 1)
No. 93, Fleet Street (south side) is endeared to us by its connection with Charles Lamb. At that number, in 1823, that great humorist, the king of all London clerks that ever were or will be, published his “Elia,” a collection of essays immortal as the language, full of quaint and tender thoughts and gleaming with cross-lights of humour as shot silk does with interchanging colours. In 1821, when the first editor was shot in a duel, the London Magazine fell into the hands of Messrs. Taylor & Hessey, of No. 93; but they published the excellent periodical and gave their “magazine dinners” at their publishing house in Waterloo Place.
Mr. John Scott, a man of great promise, the editor of the London for the first publishers— Messrs. Baldwin, Cradock, & Joy—met with a very tragic death in 1821. The duel in which he fell arose from a quarrel between the men on theLondon and the clever but bitter and unscrupulous writers in Blackwood, started in 1817. Lockhart, who had cruelly maligned Leigh Hunt and his set (the “Cockney School,” as the Scotch Tories chose to call them), was sharply attacked in the London. Fiery and vindictive Lockhart flew at once up to town, and angrily demanded from Mr. Scott, the editor, an explanation, an apology, or a meeting. Mr. Scott declined giving an apology unless Mr. Lockhart would first deny that he was editor of Blackwood. Lockhart refused to give this denial, and retorted by expressing a mean opinion of Mr. Scott’s courage. Lockhart and Scott both printed contradictory versions of the quarrel, which worked up till at last Mr. Christie, a friend of Lockhart’s, challenged Scott; and they met at Chalk Farm by moonlight on February 16th, at nine o’clock at night, attended by their seconds and surgeons, in the old business-like, bloodthirsty way. The first time Mr. Christie did not fire at Mr. Scott, a fact of which Mr. Patmore, the author, Scott’s second, with most blamable indiscretion, did not inform his principal. At the second fire Christie’s ball struck Scott just above the right hip, and he fell. He lingered till the 27th. It was said at the time that Hazlitt, perhaps unintentionally, had driven Scott to fight by indirect taunts. “I don’t pretend,” Hazlitt is reported to have said, “to hold the principles of honour which you hold. I would neither give nor accept a challenge. You hold the opinions of the world; with you it is different. As for me, it would be nothing. I do not think as you and the world think,” and so on. Poor Scott, not yet forty, had married the pretty daughter of Colnaghi, the print-seller in Pall Mall, and left two children.
For the five years it lasted, perhaps no magazine —not even the mighty Maga itself—ever drew talent towards it with such magnetic attraction. In Mr. Barry Cornwall’s delightful memoir of his old friend Lamb, written when the writer was in his seventy-third year, he has summarised the writers on the London, and shown how deep and varied was the intellect brought to bear on its production. First of all he mentions poor Scott, a shrewd, critical, rather hasty man, who wrote essays on Sir Walter Scott, Wordsworth, Godwin, Byron, Keats, Shelley, Leigh Hunt, and Hazlitt, his wonderful contemporaries, in a fruitful age. Hazlitt, glowing and capricious, produced the twelve essays of his “Table Talk,” many dramatic articles, and papers on Beckford’s Fonthill, the Angerstein pictures, and the Elgin marbles—pages wealthy with thought. Lamb contributed in three years all the matchless essays of “Elia.” Mr. Thomas Carlyle, then only a promising young Scotch philosopher, wrote several articles on the “Life and Writings of Schiller.” Mr. de Quincey, that subtle thinker and bitter Tory, contributed his wonderful “Confessions of an Opium-Eater.” That learned and amiable man, the Rev. H.F. Cary, the translator of Dante, wrote several interesting notices of early French poets. Allan Cunningham, the vigorous Scottish bard, sent the romantic “Tales of Lyddal Cross” and a series of papers styled “Traditional Literature.” Mr. John Poole—recently deceased, 1872—(the author of Paul Pry and that humorous novel, “Little Pedlington,” which is supposed to have furnished Mr. Charles Dickens with some suggestions for “Pickwick”) wrote burlesque imitations of contemporaneous dramatic writers—Morton, Dibdin, Reynolds, Moncrieff, &c. Mr. J. H. Reynolds wrote, under the name of Henry Herbert, notices of contemporaneous events, such as a scene at the Cockpit, the trial of Thurtell (a very powerful article), &c. That delightful punster and humorist, with pen or pencil, Tom Hood, sent to the London his first poems of any ambition or length—”Lycus the Centaur,” and “The Two Peacocks of Bedfont,” Keats, “that sleepless soul that perished in its pride,” and Montgomery, both contributed poems. Sir John Bowring, the accomplished linguist, wrote on Spanish poetry. Mr. Henry Southern, the editor of that excellent work the Retrospective Review, contributed “The Conversations of Lord Byron.” Mr. Walter Savage Landor, that very original and eccentric thinker, published in the extraordinary magazine one of his admirable “Imaginary Conversations.” Mr. Julius (afterwards Archdeacon) Hare reviewed the robust works of Landor. Mr. Elton contributed graceful translations from Catullus, Propertius, &c. Even among the lesser contributors there were very eminent writers, not forgetting Barry Cornwall, Hartley Coleridge, John Clare, the Northamptonshire peasant poet; and Bernard Barton, the Quaker poet. Nor must we omit that strange contrast to these pure-hearted and wise men, “Janus Weathercock” (Wainwright), the polished villain who murdered his young niece and most probably several other friends and relations, for the money insured upon their lives. This gay and evil being, by no means a dull writer upon art and the drama, was much liked by Lamb and the Russell Street set. The news of his coldblooded crimes (transpiring in 1837) seem to have struck a deep horror among all the scoundrel’s fashionable associates. Although when arrested in France it was discovered that Wainwright habitually carried strychnine about with him, he was only tried for forgery, and for that offence transported for life.
A fine old citizen of the last century, Joseph Brasbridge, who published his memoirs, kept a silversmith’s shop at No. 98, several doors from Alderman Waithman’s. At one time Brasbridge confesses he divided his time between the tavern club, the card party, the hunt, and the fight, and left his shop to be looked after by others, whilst he decided on the respective merits of Humphries and Mendoza, Cribb and Big Ben. Among Brasbridge’s early customers were the Duke of Marlborough, the Duke of Argyle, and other men of rank, and he glories in having once paid an elaborate compliment to Lady Hamilton. The most curious story in Brasbridge’s “Fruits of Experience” is the following, various versions of which have been paraphrased by modern writers. A surgeon in Gough Square had purchased for dissection the body of a man who had been hanged at Tyburn. The servant girl, wishing to look at the corpse, stole upstairs in the doctor’s absence, and, to her horror, found the body sitting up on the board, wondering where it was. The girl almost threw herself down the stairs in her fright. The surgeon, on learning of the resuscitation of his subject, humanely concealed the man in the house till he could fit him out for America. The fellow proved as clever and industrious as he was grateful, and having amassed a fortune, he eventually left it all to his benefactor. The sequel is still more curious. The surgeon dying some years after, his heirs were advertised for. A shoemaker at Islington eventually established a claim and inherited the money. Mean in prosperity, the ci-devant shoemaker then refused to pay the lawyer’s bill, and, moreover, called him a rogue. The enraged lawyer replied, “I have put you into possession of this property by my exertions, now I will spend £100, out of my own pocket to take it away again, for you are not deserving of it,” The lawyer accordingly advertised again for the surgeon’s nearest of kin; Mr. Willcocks, a bookseller in the Strand, then came forward, and deposed that his wife and her mother, he remembered, used to visit the surgeon in Gough Square. On inquiry Mrs. Willcocks was proved the next of kin, and the base shoemaker returned to his last. The lucky Mr. Willcocks was the good-natured bookseller who lent Johnson and Garrick, when they first came up to London to seek their fortunes, £5 on their joint note.

ALDERMAN WAITHMAN, FROM AN AUTHENTIC PORTRAIT (see page 68).
Nos. 103 (now the Sunday Times office) and 104 were the shop of that bustling politician Alderman Waithman; and to his memory was erected the obelisk on the site of his first shop, formerly the north-west end of Fleet Market. Waithman, according to Mr. Timbs, had a genius for the stage, and especially shone as Macbeth. He was uncle to John Reeve, the comic actor. Cobbett, who hated Waithman, has left a portrait of the alderman, written in his usual racy English. “Among these persons,” he says, talking of the Princess Caroline agitation, in 1813, “there was a common councilman named Robert Waithman, a man who for many years had taken a conspicuous part in the politics of the City; a man not destitute of the powers of utterance, and a man of sound principles also. But a man so enveloped, so completely swallowed up by self-conceit, who, though perfectly illiterate, though unable to give to three consecutive sentences a grammatical construction, seemed to look upon himself as the first orator, the first writer, and the first statesman of the whole world. He had long been the cock of the Democratic party in the City; he was a great speechmaker; could make very free with facts, and when it suited his purpose could resort to as foul play as most men.” According to Cobbett, who grows more than usually virulent on the occasion, Waithman, vexed that Alderman Wood had been the first to propose an address of condolence to the Princess at the Common Council, opposed it, and was defeated. As Cobbett says, “He then checked himself, endeavoured to recover his ground, floundered about got some applause by talking about rotten boroughs and parliamentary reform. But all in vain. Then rose cries of ‘No, no! the address—the address!’ which appear to have stung him to the quick. His face, which was none of the whitest, assumed a ten times darker die. His look was furious, while he uttered the words, ‘I am sorry that my well-weighed opinions are in opposition to the general sentiment so hastily adopted; but I hope the Livery will consider the necessity of preserving its character for purity and wisdom.'” On the appointed day the Princess was presented with the address, to the delight of the more zealous Radicals. The procession of more than one hundred carriages came back past Carlton House on their return from Kensington, the people groaning and hissing to torment the Regent.

GROUP AT HARDHAM’S TOBACCO SHOP (see page 69).
Brasbridge, the Tory silversmith of Fleet Street, writes very contemptuously in his autobiography of Waithman. Sneering at his boast of reading, he says: “I own my curiosity was a little excited to know when and where he began his studies. It could not be in his shop in Fleet Market, for there he was too busily employed in attending to the fishwomen and other ladies connected with the business of the market. Nor could it be at the corner of Fleet Street, where he was always no less assiduously engaged in ticketing his supersuper calicoes at two and two pence, and cutting them off for two and twenty pence.” According to Brasbridge, Waithman made his first speech in 1792, in Founder’s Hall, Lothbury, “called by some at that time the cauldron of sedition.” Waithman was Lord Mayor in 1823–24, and was returned to Parliament five times for the City. The portrait of Waithman on page 66, and the view of his shop, page 61, are taken from pictures in Mr. Gardiner’s magnificent collection.
A short biography of this civic orator will not be uninteresting:—Robert Waithman was born of humble parentage, at Wrexham, in North Wales. Becoming an orphan when only four months old, he was placed at the school of a Mr. Moore by his uncle, on whose death, about 1778, he obtained a situation at Reading, whence he proceeded to London, and entered into the service of a respectable linen-draper, with whom he continued till he became of age. He then entered into business at the south end of Fleet Market, whence, some years afterwards, he removed to the corner of New Bridge Street. He appears to have commenced his political career about 1792, at the oratorical displays made in admiration and imitation of the proceedings of the French revolutionists, at Founder’s Hall, in Lothbury. In 1794 he brought forward a series of resolutions, at a common hall, animadverting upon the war with revolutionised France, and enforcing the necessity of a reform in Parliament. In 1796 he was first elected a member of the Common Council for the Ward of Farringdon Without, and became a very frequent speaker in that public body. It was supposed that Mr. Fox intended to have rewarded his political exertions by the place of Receiver-General of the Land Tax. In 1818, after having been defeated on several previous occasions, he was elected as one of the representatives in Parliament of the City of London, defeating the old member, Sir William Curtis.
Very shortly after, on the 4th of August, he was elected Alderman of his ward, on the death of Sir Charles Price, Bart. On the 25th of January, 1819, he made his maiden speech in Parliament, on the presentation of a petition praying for a revision of the criminal code, the existing state of which he severely censured. At the ensuing election of 1820 the friends of Sir William Curtis turned the tables upon him, Waithman being defeated. In this year, however, he attained the honour of the shrievalty; and in October, 1823, he was chosen Lord Mayor. In 1826 he stood another contest for the City, with better success. In 1830, 1831, and 1832 he obtained his re-election with difficulty; but in 1831 he suffered a severe disappointment in losing the chamberlainship, in the competition for which Sir James Shaw obtained a large majority of votes.
We subjoin the remarks made on his death by the editor of the Times newspaper:—”The magistracy of London has been deprived of one of its most respectable members, and the City of one of its most upright representatives. Everybody knows that Mr. Alderman Waithman has filled a large space in City politics; and most people who were acquainted with him will be ready to admit that, had his early education been better directed, or his early circumstances more favourable to his ambition, he might have become an important man in a wider and higher sphere. His natural parts, his political integrity, his consistency of conduct, and the energy and perseverance with which he performed his duties, placed him far above the common run of persons whose reputation is gained by their oratorical displays at meetings of the Common Council. In looking back at City proceedings for the last thirty-five or forty years, we find him always rising above his rivals as the steady and consistent advocate of the rights of his countrymen and the liberties and privileges of his fellow-citizens.”
There is a curious story told of the Fleet Street crossing, opposite Waithman’s corner. It was swept for years by an old black man named Charles M’Ghee, whose father had died in Jamaica at the age of 108. According to Mr. Noble, when he laid down his broom he sold his professional right for £1,000 (£100 ?). Retiring into private life much respected, he was always to be seen on Sundays at Rowland Hill’s chapel. When in his seventy third year his portrait was taken and hung in the parlour of the “Twelve Bells,” Bride Lane. To Miss Waithman, who used to send him out soup and bread, he is, untruly, said to have left. £7,000.
Mr. Diprose, in his “History of St. Clement,” tells us more of this black sweeper. “Brutus Billy,” or “Tim-buc-too,” as he was generally called, lived in a passage leading from Stanhope Street into Drury Lane. He was a short, thick-set man, with his white-grey hair carefully brushed up into a toupee, the fashion of his youth. He was found in his shop, as he called his crossing, in all weathers, and was invariably civil. At night, after he had shut up shop (swept mud over his crossing), he carried round a basket of nuts and fruit to places of public entertainment, so that in time he laid by a considerable amount of money. Brutus Billy was brimful of story and anecdote. He died in Chapel Court in 1854, in his eighty-seventh year. This worthy man was perhaps the model for Billy Waters, the negro beggar in Tom and Jerry, who is so indignant at the beggars’ supper on seeing “a turkey without sassenges.”
In Garrick’s time John Hardham, the wellknown tobacconist, opened a shop at No. 106. There, at the sign of the “Red Lion,” Hardham’s Highlander kept steady guard at a doorway through which half the celebrities of the day made their exits and entrances. His celebrated “No. 37” snuff was said, like the French millefleur, to be composed of a great number of ingredients, and Garrick in his kind way helped it into fashion by mentioning it favourably on the stage. Hardham, a native of Chichester, began life as a servant, wrote a comedy, acted, and at last became Garrick’s “numberer,” having a general’s quick coup d’æil at gauging an audience, and so checking the money-takers. Garrick once became his security for a hundred pounds, but eventually Hardham grew rich, and died in 1772, bequeathing £22,289 to Chichester, 10 guineas to Garrick, and merely setting apart £10 for his funeral, only vain fools, as he said, spending more. We can fancy the great actors of that day seated on Hardham’s tobacco-chests discussing the drollery of Foote or the vivacity of Clive.
“It has long been a source of inquiry,” says a writer in the City Press, “whence the origin of the cognomen, ‘No. 37,’ to the celebrated snuff compounded still under the name of John Hardham, in Fleet Street. There is a tradition that Lord Townsend, on being applied to by Hardham, whom he patronised, to name the snuff, suggested the cabalistic number of 37, it being the exact number of a majority obtained in some proceedings in the Irish Parliament during the time he was Lord Lieutenant there, and which was considered a triumph for his Government. The dates, however, do not serve this theory, as Lord Townsend was not viceroy till the years 1767–72, when the snuff must have been well established in public fame and Hardham in the last years of his life. It has already been printed elsewhere that, on the famed snuff coming out in the first instance, David Garrick, hearing of it, called in Fleet Street, as he was wont frequently to do, and offered to bring it under the public notice in the most effectual manner, by introducing an incident in a new comedy then about to be produced by him, where he would, in his part in the play, offer another character a pinch of snuff, who would extol its excellence, whereupon Garrick arranged to continue the conversation by naming the snuff as the renowned ’37 of John Hardham.’ But the enigma, even now, is not solved; so we will, for what it may be worth, venture our own explanation. It is well known that in most of the celebrated snuffs before the public a great variety of qualities and descriptions of tobacco, and of various ages, are introduced. Hardham, like the rest, never told his secret how the snuff was made, but left it as a heritage to his successors. It is very probable, therefore, that the mystic figures, 37, we have quoted represented the number of qualities, growths, and description of the ‘fragrant weed’ introduced by him into his snuff, and may be regarded as a sort of appellative rebus, or conceit, founded thereon.” (fn. 2)
But Hardham occupied himself in other ways than in the making of snuff and of money—for the Chichester youth had now grown wealthy—and in extending his circle of acquaintances amongst dramatists and players; he was abundantly distinguished for Christian charity, for, in the language of a contemporary writer, we find that “his deeds in that respect were extensive,” and his bounty “was conveyed to many of the objects of it in the most delicate manner.” From the same authority we find that Hardham once failed in business (we presume, as a lapidary) more creditably than he could have made a fortune by it. This spirit of integrity, which remained a remarkable feature in his character throughout life, induced him to be often resorted to by his wealthy patrons as trustee for the payment of their bounties to deserving objects; in many cases the patrons died before the recipients of their relief. With Hardham, however, this made no difference; the annuities once granted, although stopped by the decease of the donors, were paid ever after by Hardham so long as he lived; and his delicacy of feeling induced him even to persuade the recipients into the belief that they were still derived from the same source.
No. 102 (south) was opened as a shop, in 1719, by one Lockyer, who called it “Mount Pleasant.” It then became a “saloop-house,” where the poor purchased a beverage made out of sassafras chips. The proprietor, who began life, as Mr. Noble says, with half-a-crown, died in March, 1739, worth £1,000. Thomas Read was a later tenant. Charles Lamb mentions “saloop” in one of his essays, and says, “Palates otherwise not uninstructed in dietetical elegancies sup it up with avidity.” Chimneysweeps, beloved by Lamb, approved it, and eventually stalls were set up in the streets, as at present to reach even humbler customers.